Valid 98-366 Dumps shared by PassLeader for Helping Passing 98-366 Exam! PassLeader now offer the newest 98-366 VCE dumps and 98-366 PDF dumps, the PassLeader 98-366 exam questions have been updated and ANSWERS have been corrected, get the newest PassLeader 98-366 dumps with VCE and PDF here: https://www.passleader.com/98-366.html (220 Q&As Dumps –> 261 Q&As Dumps)
BTW, DOWNLOAD part of PassLeader 98-366 dumps from Cloud Storage: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpVVhXZTVKdDJpSnc
QUESTION 1
A router’s static route is set by the ____.
A. adjacent network
B. next upstream router
C. network administrator
D. routing protocol
Answer: C
Explanation:
Static routing is a form of routing that occurs when a router uses a manually-configured routing entry, rather than information from a dynamic routing protocol to forward traffic.
QUESTION 2
Which setting is used to determine the Domain Name System (DNS) settings on a client computer?
A. TELNET
B. NSLOOKUP
C. PATHPING
D. NETSTAT
Answer: B
Explanation:
NSLOOKUP is a network administration command-line tool available for many computer operating systems for querying the Domain Name System (DNS) to obtain domain name or IP address mapping or for any other specific DNS record.
QUESTION 3
The host name of the fully qualified domain name (FQDN) mail.exchange.corp.nwtraders.com is ____.
A. corp
B. com
C. nwtraders
D. exchange
E. mail
Answer: E
Explanation:
Hostnames are composed of series of labels concatenated with dots, as are all domain names. For example, let’s break mail.google.com into its component parts: mail is the host or local hostname; and google.com is the domain or parent domain name.
QUESTION 4
To which IP configuration does the CIDR notation 192.168.1.1/25 refer?
A. 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.64
B. 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.1
C. 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.32
D. 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.256
E. 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.128
Answer: E
Explanation:
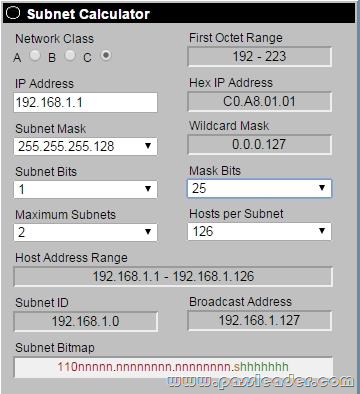
http://www.subnet-calculator.com/
QUESTION 5
Which command is used to verify that a server is connected to the network?
A. IPCONFIG
B. ROUTE
C. PING
D. CHECK
Answer: C
Explanation:
PING is a computer network administration software utility used to test the reachability of a host on an Internet Protocol (IP) network and to measure the round-trip time for messages sent from the originating host to a destination computer.
QUESTION 6
Which of these represents the Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) loopback address?
A. 127.0.0.1
B. 192.168.0.1
C. FEC0:A8C0::AA01
D. ::1
Answer: D
Explanation:
The localhost (loopback) address, 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, and the IPv6 unspecified address, 0:0:0:0:0:0:0:0, are reduced to ::1 and ::, respectively.
QUESTION 7
Which of these addresses is a multicast address?
A. 127.0.0.1
B. 169.254.0.1
C. 192.168.0.1
D. 224.0.0.1
Answer: D
Explanation:
The full range of multicast addresses is from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255.
QUESTION 8
Which of the following uses Pointer records and A records?
A. IDS
B. DNS Server
C. NAT Server
D. IPS
Answer: B
Explanation:
DNS records include:
* A: Address record.
* PTR: Pointer record.
QUESTION 9
The ipconfig command will ____.
A. configure routers
B. display a client’s address
C. display a client’s broadcast mode
D. configure DHCP clients
Answer: B
Explanation:
Displays all current TCP/IP network configuration values and refreshes Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) and Domain Name System (DNS) settings. Used without parameters, ipconfig displays the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway for all adapters.
QUESTION 10
One reason to incorporate VLANs in a network is to ____.
A. increase the number of available IP addresses
B. increase the number of available Media Access Control (MAC) addresses
C. reduce the number of broadcast domains
D. reduce the number of nodes in a broadcast domain
Answer: D
Explanation:
VLANs provide the following advantages:
* VLANs enable logical grouping of end-stations that are physically dispersed on a network.
* VLANs reduce the need to have routers deployed on a network to contain broadcast traffic.
* Confinement of broadcast domains on a network significantly reduces traffic.
By confining the broadcast domains, end-stations on a VLAN are prevented from listening to or receiving broadcasts not intended for them. Moreover, if a router is not connected between the VLANs, the end- stations of a VLAN cannot communicate with the end-stations of the other VLANs.
QUESTION 11
Which of these is an application layer protocol?
A. TCP
B. FTP
C. IP
D. UDP
Answer: B
Explanation:
FTP is an application layer protocol.
QUESTION 12
The top-level domain of www.adventureworks.com is ____.
A. www
B. adventureworks
C. adventureworks.com
D. com
Answer: D
Explanation:
A top-level domain (TLD) is one of the domains at the highest level in the hierarchical Domain Name System of the Internet.
QUESTION 13
At what layer in the OSI model are hardware addresses referenced?
A. Network
B. Application
C. Data link
D. Physical
Answer: C
QUESTION 14
You need to divide a network into three subnets. Which device should you use?
A. Hub
B. Bridge
C. Router
D. Segmenter
Answer: C
Explanation:
You can use a router to divide your network into subnets.
QUESTION 15
The type of connector used on a 100BaseT Ethernet cable is ____.
A. RJ-11
B. RJ-45
C. TNC
D. BNC
Answer: B
QUESTION 16
In addition to switching, multilayer switches also ____.
A. Provide Layer 3 routing functions
B. Interface with CAT3, CAT5, CAT5e, and fiber optics
C. Support 10 MB, 100 MB, and 1 GB local area network (LAN) ports
D. Operate by using only Layer 1 and 2 protocols
Answer: A
QUESTION 17
One reason to replace an unmanaged switch with a managed switch is to ____.
A. manage the routing tables
B. support multiple VLANS
C. reduce collision domains
D. route between networks
Answer: B
Explanation:
A multilayer switch (MLS) is a computer networking device that switches on OSI layer 2 like an ordinary network switch and provides extra functions on higher OSI layers. The major difference between the packet switching operation of a router and that of a Layer 3 switch is the physical implementation. In general-purpose routers, packet switching takes place using software that runs on a microprocessor, whereas a Layer 3 switch performs this using dedicated application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) hardware.
QUESTION 18
To directly connect the Ethernet network interface cards (NICs) of two computers, you should use a ____.
A. crossover cable
B. straight cable
C. rollover cable
D. coaxial cable
Answer: A
Explanation:
An Ethernet crossover cable is a type of Ethernet cable used to connect computing devices together directly. Normal straight through cables were used to connect from a host network interface controller (a computer or similar device) to a network switch, hub or router.
QUESTION 19
The function of a router is to ____.
A. provide IP subnet masks for hosts
B. forward traffic to other networks
C. broadcast routing tables to clients
D. store tables for name resolution
Answer: B
Explanation:
A router is a device that forwards data packets along networks. A router is connected to at least two networks, commonly two LANs or WANs or a LAN and its ISP’s network. Routers are located at gateways, the places where two or more networks connect.
QUESTION 20
If a router cannot determine the next hop for a packet, the router will ____.
A. forward the packet to the default route
B. send the packet back to the packet’s source
C. broadcast the packet
D. store the packet in the memory buffer
Answer: A
Explanation:
If there is no next hop, the packets are not policy routed. A default route of a computer that is participating in computer networking is the packet forwarding rule (route) taking effect when no other route can be determined for a given Internet Protocol (IP) destination address.
Get the newest PassLeader 98-366 VCE dumps here: https://www.passleader.com/98-366.html (220 Q&As Dumps –> 261 Q&As Dumps)
And, DOWNLOAD the newest PassLeader 98-366 PDF dumps from Cloud Storage for free: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpVVhXZTVKdDJpSnc