Valid 98-366 Dumps shared by PassLeader for Helping Passing 98-366 Exam! PassLeader now offer the newest 98-366 VCE dumps and 98-366 PDF dumps, the PassLeader 98-366 exam questions have been updated and ANSWERS have been corrected, get the newest PassLeader 98-366 dumps with VCE and PDF here: https://www.passleader.com/98-366.html (220 Q&As Dumps –> 261 Q&As Dumps)
BTW, DOWNLOAD part of PassLeader 98-366 dumps from Cloud Storage: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpVVhXZTVKdDJpSnc
QUESTION 141
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct. Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select ‘No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
All session data is encrypted between all machines while using telnet.
A. Not encrypted
B. Encrypted between any Windows machines
C. Encrypted only to any non-Windows machines
D. No change is needed
Answer: A
Explanation:
Telnet, by default, does not encrypt any data sent over the connection (including passwords), and so it is often practical to eavesdrop on the communications and use the password later for malicious purposes; anybody who has access to a router, switch, hub or gateway located on the network between the two hosts where Telnet is being used can intercept the packets passing by and obtain login, password and whatever else is typed with a packet analyzer.
QUESTION 142
Which protocol is a transport layer protocol?
A. FTP
B. IP
C. UDP
D. ASCII
Answer: C
Explanation:
Transport layer protocols include: UDP, TCP.
QUESTION 143
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct. Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select “No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
IPv4 multicast addresses range from 192.168.0.0 to 192.168.255.255.
A. 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255
B. 172.16.0.0 to 172.31.255.255
C. 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255
D. No change is needed
Answer: C
Explanation:
Class D is multicast.
Class A: 0.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255
Class B: 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255
Class C: 192.0.0.0 – 223.255.255.255
Class D: 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255
QUESTION 144
This question requires that you evaluate the underlined text to determine if it is correct. Select the correct answer if the underlined text does not make the statement correct. Select ‘No change is needed” if the underlined text makes the statement correct.
The four IEEE standards, 802.11a, b, g, and n, are collectively known as mobile ad hoc networks.
A. WiMAX
B. Bluetooth
C. WiFi
D. No change is needed
Answer: C
Explanation:
IEEE 802.11 is a set of media access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication in the 2.4, 3.6, 5, and 6 GHz frequency bands. They are created and maintained by the IEEE LAN/MAN Standards Committee (IEEE 802). The base version of the standard was released in 1997, and has had subsequent amendments. The standard and amendments provide the basis for wireless network products using the Wi-Fi brand.
QUESTION 145
Hotspot
You cannot get to any site on the Internet or on the school’s intranet. Your school uses DHCP. You check your network settings, which are configured as shown in the following image:
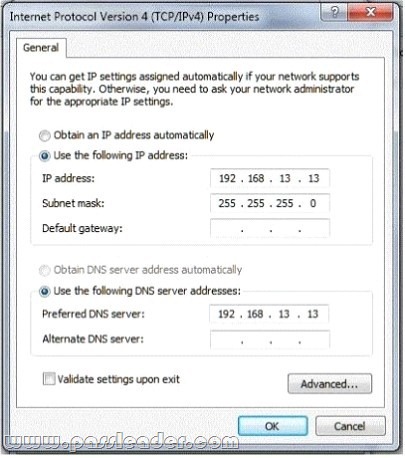
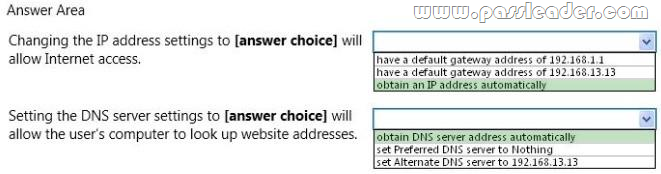
You need to change the settings to access websites. Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement. Each correct selection is worth one point.

Answer:
Explanation:
The configuration must be set to obtain both IP and DNS server address automatically.
QUESTION 146
A university has network links between various locations. Where would a T3 connection be appropriate?
A. Server to network in the main campus server room
B. Main campus to a large satellite campus
C. Computer lab PC to lab printer
D. Library laptop PC to Internet
Answer: A
Explanation:
T3 lines are a common aggregation of 28 T1 circuits that yields 44.736 Mbps total network bandwidth. Besides being used for long-distance traffic, T3 lines are also often used to build the core of a business network at its headquarters.
QUESTION 147
Drag and Drop
Match each network type to its corresponding definition. To answer, drag the appropriate network type from the column on the left to its definition on the right. Each network type may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Each correct match is worth one point.

Answer:

Explanation:
– An extranet is a computer network that allows controlled access from outside of an organization’s intranet. Extranets are used for specific use cases including business-to-business (B2B).
– An intranet is a private network that is contained within an enterprise.
– The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks.
QUESTION 148
Drag and Drop
Match the VPN connection type to the corresponding definition. To answer, drag the appropriate VPN term from the column on the left to its definition on the right. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Each correct match is worth one point.

Answer:
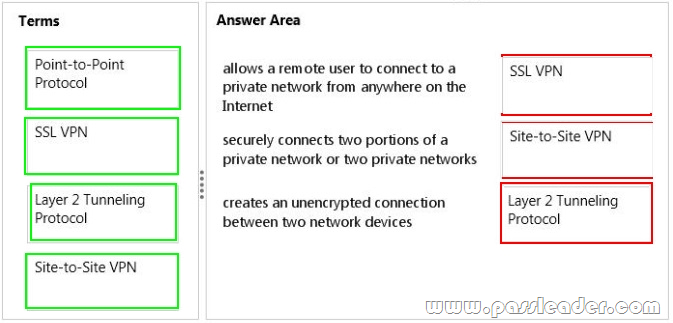
Explanation:
– An SSL VPN (Secure Sockets Layer virtual private network) is a form of VPN that can be used with a standard Web browser. In contrast to the traditional Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) VPN, an SSL VPN does not require the installation of specialized client software on the end user’s computer. It’s used to give remote users with access to Web applications, client/server applications and internal network connections.
– A site-to-site VPN allows offices in multiple fixed locations to establish secure connections with each other over a public network such as the Internet.
– Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP) is a tunneling protocol used to support virtual private networks (VPNs) or as part of the delivery of services by ISPs. It does not provide any encryption or confidentiality by itself.
QUESTION 149
Drag and Drop
Match each set of characteristics to the corresponding 802.11 standard. To answer, drag the appropriate set of characteristics from the column on the left to its 802.11 standard on the right. Each set may be used once, more than once, or not at all. Each correct match is worth one point.

QUESTION 150
A Media Access Control (MAC) address identifies a/an ____.
A. UPnP device
B. Local broadcast domain
C. Network interface card (NIC)
D. Local area network (LAN)
Answer: C
Explanation:
A media access control address (MAC address) is a unique identifier assigned to network interfaces for communications on the physical network segment.
QUESTION 151
Two companies want to share data by using the Internet. Which type of network provides the solution?
A. Ethernet
B. Intranet
C. Extranet
D. Perimeter
Answer: C
Explanation:
An extranet is a computer network that allows controlled access from outside of an organization’s intranet. Extranets are used for specific use cases including business-to-business (B2B).
QUESTION 152
A VPN is a/an ____.
A. encrypted connection across the Internet
B. virtual network within your Local Area Network (LAN)
C. communication tunnel between VLANs
D. personal network for your use only
Answer: A
QUESTION 153
Which of the following determines the media access method that is used in a network?
A. Number of hosts connected to the network
B. Number of domain servers on the segment
C. Maximum speed of the media
D. Topology and protocols
Answer: D
QUESTION 154
Which wireless authentication method provides the highest level of security?
A. Wired Equivalency Privacy (WEP)
B. IEEE 802.11n
C. WI-FI Protected Access (WPA)
D. IEEE 802.11a
Answer: C
Explanation:
WPA aims to provide stronger wireless data encryption than WEP. Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) is a security protocol and security certification program developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance to secure wireless computer networks.
QUESTION 155
The topology of a local area network (LAN) is defined by the ____.
A. number of devices to connect
B. physical and logical characteristics
C. distance between workstations
D. type of cable being used
Answer: B
Explanation:
Network topology is the arrangement of the various elements (links, nodes, etc.) of a computer network. Essentially, it is the topological structure of a network and may be depicted physically or logically.
QUESTION 156
The maximum throughput of an 802.11g network is ____.
A. 2.4 GHz.
B. 5.4 GHz.
C. 11 Mbps
D. 54 Mbps.
Answer: D
Explanation:
The 802.11g standard for wireless networking supports a maximum bandwidth of 54 Mbps.
QUESTION 157
A node within a local area network (LAN) must have a network interface device and a ____.
A. network account
B. table of all network nodes
C. host address
D. resource to share
Answer: C
Explanation:
In network addressing, the host address, or the host ID portion of an IP address, is the portion of the address used to identify hosts (any device requiring a Network Interface Card, such as a PC or networked printer) on the network.
QUESTION 158
Which of the following is a Layer 2 WAN protocol?
A. Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP)
B. Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
C. Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
D. Internet Protocol (IP)
Answer: A
Explanation:
WAN Protocols and Their Corresponding OSI Layers:

QUESTION 159
Which type of port is used to support VLAN traffic between two switches?
A. Virtual port
B. WAN port
C. Trunk port
D. LAN port
Answer: C
Explanation:
Trunk links are required to pass VLAN information between switches.
QUESTION 160
The protocol that maps IP addresses to a Media Access Control (MAC) address is ____.
A. Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP)
B. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
C. Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
D. User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
E. Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
Answer: E
Explanation:
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol for mapping an Internet Protocol address (IP address) to a physical machine address (MAC address) that is recognized in the local network.
Get the newest PassLeader 98-366 VCE dumps here: https://www.passleader.com/98-366.html (220 Q&As Dumps –> 261 Q&As Dumps)
And, DOWNLOAD the newest PassLeader 98-366 PDF dumps from Cloud Storage for free: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpVVhXZTVKdDJpSnc
