Valid 70-341 Dumps shared by PassLeader for Helping Passing 70-341 Exam! PassLeader now offer the newest 70-341 VCE dumps and 70-341 PDF dumps, the PassLeader 70-341 exam questions have been updated and ANSWERS have been corrected, get the newest PassLeader 70-341 dumps with VCE and PDF here: http://www.passleader.com/70-341.html (261 Q&As Dumps –> 272 Q&As Dumps)
BTW, DOWNLOAD part of PassLeader 70-341 dumps from Cloud Storage: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpfjZ2U1ZfVEZvU0ZreTJkNG1xdmxjS0xUYkdHWVMxWFNRVDhOYTlyRzBjOXM
QUESTION 181
You deploy an Exchange Server 2013 organization to a test network for evaluation. You install the Mailbox server role and the Client Access server role on a server named ex01.contoso.com. You do not perform any other configurations. All of the ports from the Internet to ex01.contoso.com are open. You successfully connect to ex01.contoso.com from the Internet and from the internal network. You need to identify which types of Exchange Server clients will connect successfully to the organization without any further configurations. What should you identify?
A. internal Outlook Web App connections
B. Android Phones using Activesync
C. Windows RT devices running the Mail app
D. Windows Phones that use Exchange ActiveSync
Answer: A
Explanation:
Not B
All Android Phones require the AllowNonProvisionableDevices parameter set to $True to sync successfully out of box with Exchange 2013 and this parameter is set to $false by default.
Not C
All Windows RT devices running the mail App require the AllowNonProvisionableDevices parameter set to $True to sync successfully out of box with Exchange 2013 and this parameter is set to $false by default.
Not D
All Windows Phones require the AllowNonProvisionableDevices parameter set to $True to sync successfully out of box with Exchange 2013 and this parameter is set to $false by default. The AllowNonProvisionableDevices parameter specifies whether all mobile phones can synchronize with the server running Exchange. When set to $true, the AllowNonProvisionableDevices parameter enables all mobile phones to synchronize with the Exchange server, regardless of whether the phone can enforce all the specific settings established in the Exchange ActiveSync policy. This also includes mobile phones managed by a separate device management system. When set to $false, this parameter blocks mobile phones that aren’t provisioned from synchronizing with the Exchange server. The default value is $false.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-gb/library/bb123756(v=exchg.141).aspx
http://exchangeserverpro.com/activesync-policies-cause-test-activesyncconnectivity-to-fail/
QUESTION 182
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. You create a public folder. You assign an email address to the public folder. You need to ensure that only a user named User1 can add content to the public folder by using email. Which cmdlet should you run?
A. Set-MailPublkFolder
B. Set-PublicFolder
C. Set-Mailbox
D. Add-PublicFolderCMentPermission
Answer: A
Explanation:
Set-MailPublicFolder.
This cmdlet is available in on-premises Exchange Server 2013 and in the cloud-based service. Use the Set-MailPublicFolder cmdlet to configure the mail-related settings of mail-enabled public folders. If you want to configure basic settings that aren’t mail related, use the Set-PublicFolder cmdlet.
EXAMPLE 1
Set-MailPublicFolder -Identity [email protected] -AcceptMessagesOnlyFrom “User1”
EXAMPLE 2
This example sets the primary SMTP address of the mail-enabled public folder [email protected] to [email protected].
Set-MailPublicFolder -Identity [email protected] -PrimarySmtpAddress [email protected]
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa997560(v=exchg.150).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb123707(v=exchg.150).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-gb/library/bb397214(v=exchg.150).aspx
QUESTION 183
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains 20 servers. You plan to deploy Exchange Server 2013 RTM Cumulative Update 1 (CU1) to the first Exchange server in the organization. You need to ensure that a user named ExehangeAdmin can deploy CU1 to the first server. The solution must minimize the number of permissions assigned to ExehangeAdmin. To which groups should you add ExehangeAdmin?
A. Schema Admins, Domain Admins, and Enterprise Admins
B. Schema Admins, Domain Admins, and Delegated Setup
C. Domain Admins and Organization Management
D. Enterprise Admins and Organization Management
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/exdeploy2013/Checklist?state=2419-W-CABEAgAAQAAAAUEAAQAAAAg~
A: Both Schema Admins and Enterprise Admins membership is needed to update the schema and prepare AD.
NOT B: Delegated Setup can be used to install the 2nd server, not the first.
NOT C: Both Schema Admins and Enterprise Admins membership is needed to update the schema and prepare AD. The user account installing the server is added to the Organization Management group during installation.
NOT D: Both Schema Admins and Enterprise Admins membership is needed to update the schema and prepare AD. The user account installing the server is added to the Organization Management group during installation.
QUESTION 184
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. An Active Directory administrator is concerned about the permissions assigned to a group named Exchange Trusted Subsystem. Exchange Trusted Subsystem has a member named Exchange Windows Permissions. You need to show the Active Directory administrator all of the permissions assigned to Exchange Trusted Subsystem. What should you use?
A. ADSI Edit
B. Active Directory Sites and Services
C. Dsget
D. Active Directory Users and Computers
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc773354(v=WS.10).aspx
QUESTION 185
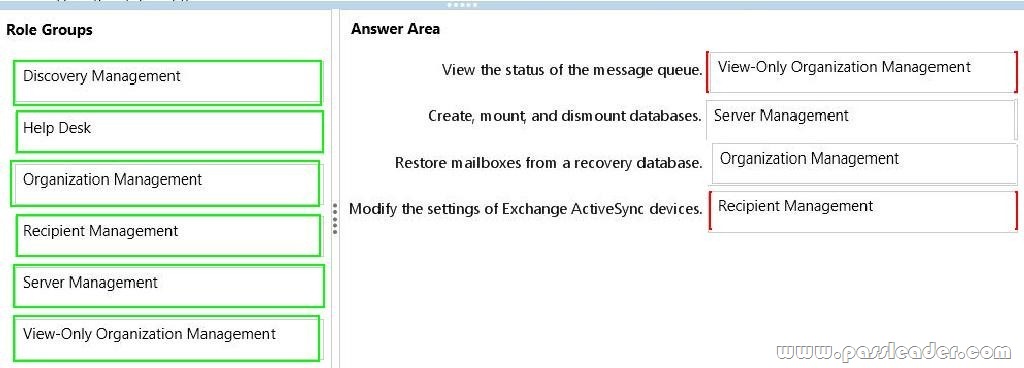
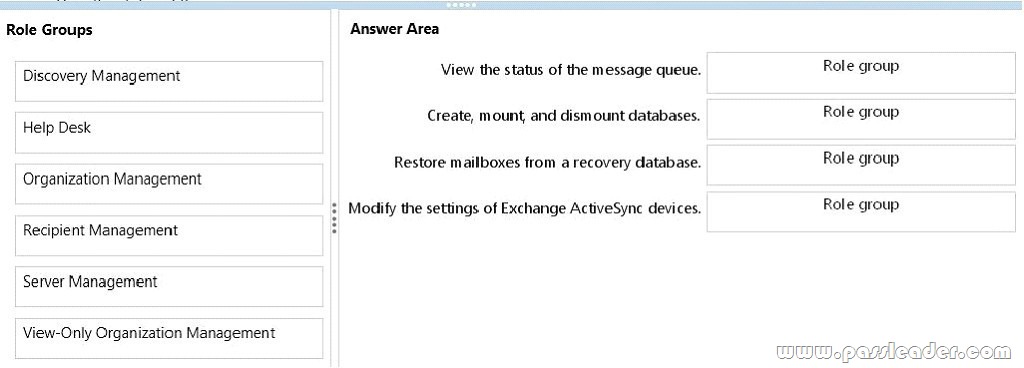
Drag and Drop Question You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. You plan to delegate the following administrative tasks:
– View the status of the message queue.
– Create, mount, and dismount databases.
– Restore mailboxes from a recovery database.
– Modify the settings of Exchange ActiveSync devices.
You need to identify which role group must be used to delegate each administrative task. The solution must ensure that the role group that has the fewest administrative privileges is used. Which role groups should you identify? (To answer, drag the appropriate role groups to the correct tasks. Each role group may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.)
QUESTION 186
Hotspot Question
Your network contains three Exchange Server 2013 servers that have the Client Access server role installed. Each server is configured as a POP3 server and an IMAP4 server. You deploy the Network Load Balancing (NLB) feature on the servers and configure NLB as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
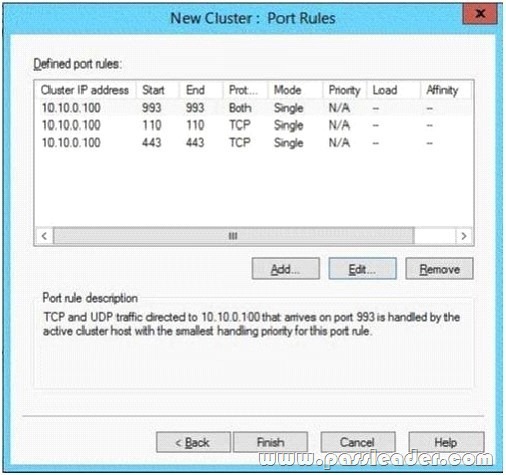
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement.

QUESTION 187
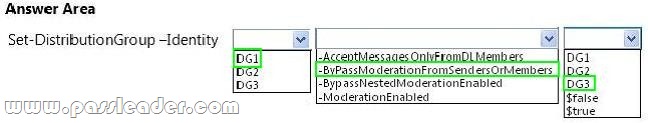
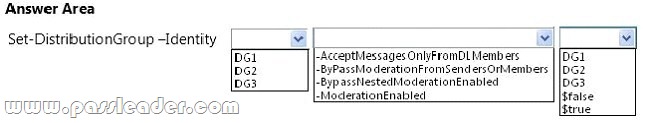
Hotspot Question
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains three moderated distribution groups named DG1, DG2, and DG3. DG3 is a member of DG2. You need to exclude from moderation the email messages sent from the members of DG3 to the members of DG1. The solution must maintain moderation for the email messages sent from all other users. What command should you run? (To answer, select the appropriate options in the answer area.)
QUESTION 188
You have an Exchange Server organization. The organization contains a server named EX01 that has Exchange Server 2010 installed and a server named EX02 that has Exchange Server 2013 installed. Your mailbox is hosted on EX01. You need to access the Exchange Adrnin Center (EAC). Which URL should you use?
A. https://EX01/ecp?ExchClientVer=14
B. https://EX02/ecp?ExchClientVer=15
C. https://EX02/eac?ExchClientVer=15
D. https://EX01/ecp?ExchCfientVer=15
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://www.cgoosen.com/2013/07/how-to-access-exchange-admin-center-eac-in-exchange-2013-during-coexistence/
http://consulting.risualblogs.com/blog/2013/06/26/exchange-2013-coexistence-ecp-redirects-to-2010-ecp-2/
http://msexchangeguru.com/2013/01/16/eac-exchange-2013/
http://blogs.technet.com/b/meamcs/archive/2013/05/04/exchange-2013-coexistence-ecp-your-mailbox-can-t-be-accessed-using-the-address-you-entered-please-obtain-the-correct-address.aspx
QUESTION 189
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. The organization contains four servers in the same Active Directory site. The servers are configured as shown in the following table. EXB and EX4 are members of a database availability group (DAG) named DAG1. All users use Microsoft Outlook 2013 to connect to their mailbox. You need to recommend a client access solution to ensure that all of the users can connect to their mailbox if EX1 or EX2 fails. What should you recommend?
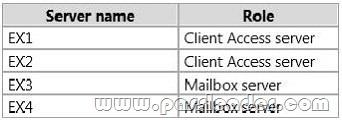
A. Add a layer 4 hardware load balancer that balances RPC traffic.
B. Add a layer 7 hardware load balancer that balances the traffic on port 443.
C. Add a layer 7 hardware load balancer that balances RPC traffic.
D. Replicate all of the databases in DAG1 to both DAG1 members.
Answer: B
Explanation:
In Exchange 2013, RPC over TCP has been disabled. All outlook communications are now through RPC over HTTP (Outlook Anywhere). This unifies the CAS protocol methods and provides a stable and reliable connectivity network between clients and server and between CAS and Mailbox Server. It also reduces the number of namespaces required. It also eliminates end user interruptions. Hence moving mailboxes around in DAG and moving mailboxes between mailbox databases are now easy.
http://blog.loadbalancer.org/load-balancing-exchange-2013/
http://windowsitpro.com/blog/exchange-2013-dumps-cas-arrays
QUESTION 190
Your company has a main office and three branch offices. The main office is located in Austin. The branch offices are located in Denver, San Diego, and Chicago. The network contains an Active Directory forest. The forest contains a single domain. Each office is configured as an Active Directory site. The site in Austin contains four domain controllers that run Windows Server 2008 R2 and are configured as global catalog servers. The sites in Denver, San Diego, and Chicago each contain a read-only domain controller (RODC) that runs Windows Server 2008 R2. No other domain controllers exist on the network. You plan to deploy an Exchange Server 2013 organization. Exchange Server 2013 servers will be deployed in the Austin, Denver, and San Diego sites. Users from the Chicago site will access their mailbox remotely. You need to recommend changes to the Active Directory infrastructure to support the planned deployment of Exchange Server 2013. What should you recommend?
A. Replace the RODCs in the Denver and San Diego sites with domain controllers that are configured as global catalog servers.
B. Configure the RODCs in the Denver and San Diego sites as read-only global catalog servers.
C. Configure Active Directory automatic site coverage for the Chicago site.
D. Upgrade all of the RODCs to Windows Server 2012.
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/aa996719.aspx
There must be a writable copy of the global catalog at each site where an Exchange 2013 server is to be installed.
QUESTION 191
How would you disable the anti malware filtering and ensure that engine updates from microsoft are downloaded and updated.
A. Disable-Antimalwareagent.ps1
B. Set-malwarefilteringserver
C. Disable-Antimalwarescanning.ps1 (probable option)
D. Update-MalwareFilteringServer.ps1 (guessed option)
Answer: B
Explanation:
Disable or Bypass Anti-Malware Scanning.
Applies to: Exchange Server 2013.
In Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, you can disable or bypass malware filtering of all email messages in transit on a server. This must be done on a Mailbox server. You may want to disable Exchange 2013 malware filtering if you are using another product for malware filtering. When malware filtering is disabled, the Exchange malware agent is unhooked and not running, and engine updates are not kept up-to-date.
Important:
Bypassing malware filtering should only be done when troubleshooting a problem. When malware filtering is bypassed, the Exchange malware agent remains hooked, and engine updates are kept up-to-date. However, malware filtering is skipped while you attempt to resolve whatever problems you are encountering. After you have finished troubleshooting, you should restore malware filtering.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj150526(v=exchg.150).aspx
http://www.ntweekly.com/?p=2813
QUESTION 192
You need to install and configure anti-spam and antimalware filtering. Which servers should you install the anti-spam agents and enable the anti-spam and antimalware filtering? (Choose two.)
A. You should install the anti-spam agents on the Client Access Servers only.
B. You should install the anti-spam agents on the Mailbox servers only.
C. You should install the anti-spam agents on the Client Access Servers and the Mailbox Servers.
D. You should enable antimalware filtering on the Client Access Servers only.
E. You should enable antimalware filtering on the Mailbox servers only.
F. You enable antimalware filtering on the Client Access Servers and the Mailbox Servers.
Answer: BE
Explanation:
http://howexchangeworks.com/2013/06/connection-filtering-in-exchange-2013.html
In Exchange 2013, the anti-spam agents can only be installed on the Mailbox role. But, the connection filtering which is very useful in fighting spam emails is not available in 2013. Same goes for the attachment filter. Even though CAS proxies emails back and forth (if setup correctly), it is a stateless proxy and can’t have any anti-spam agents on it.
http://www.jaapwesselius.com/2013/01/10/installing-exchange-server-2013-part-iii/
In Exchange 2013 the anti-spam functionality (through protocol agents) is running on the Mailbox Server and not on the Client Access Server so all mail, including all spam will hit the Mailbox Server when installed in a configuration as outlined in these blog post series. The anti-spam functionality is enabled using a Powershell script (.\EnableAntiSpamAgents.ps1) and offers Sender and Recipient filtering, content filtering, Sender Reputation and Sender ID filtering. To activate the ant-spam agents on the Mailbox Server open the Exchange Management Shell and enter the following commands:
CD $Exscripts.\Install-AntiSpamAgents.ps1
http://www.tlglearning.com/LinkClick.aspx?fileticket=dnonu0glRr8%3D&tabid=238
You can’t enable the anti-spam agents on an Exchange 2013 Client Access Server.
https://social.technet.microsoft.com/Forums/exchange/en-US/5c9f1b51-4a93-4de4-964e-1f53afbb8e8b/how-to-configure-attachment-filter-agent-on-exchange-2013-
The Malware Filter runs on every 2013 Mailbox server to protect against malware and viruses.
http://blogs.dirteam.com/blogs/davestork/archive/2012/12/06/exchange-and-malware-protection.aspx
QUESTION 193
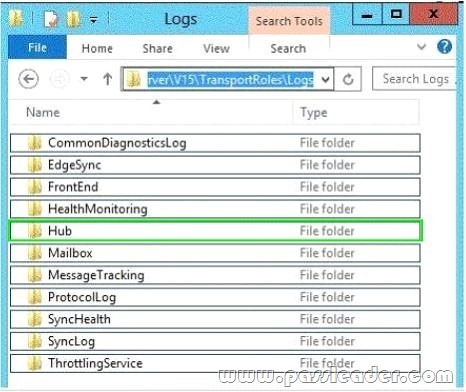
Hotspot Question
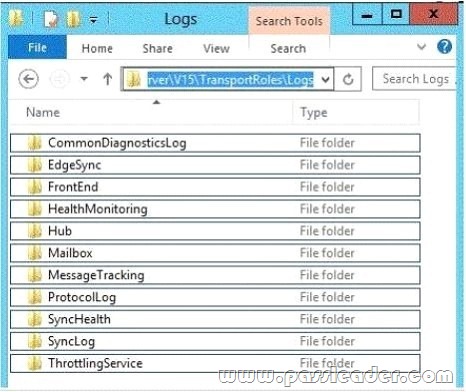
Your company has an Exchange Server 2013 organization. You configure domain security with a partner organization. You configure the required connectors. You plan to verify whether the partner organization configured the required settings for domain security. You enable logging for the Send connectors and the Receive connectors. You need to verify that the STARTTLS command is issued by an Exchange server when an email message is sent to the partner organization. Which log folder should you review? (To answer, select the appropriate folder in the answer area.)
QUESTION 194
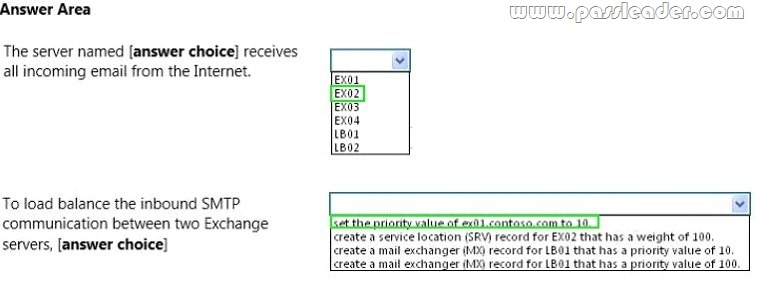
Hotspot Question
Your company has an Exchange Server 2013 organization. All servers have the Client Access server role and the Mailbox server role installed. The DNS Manager is shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
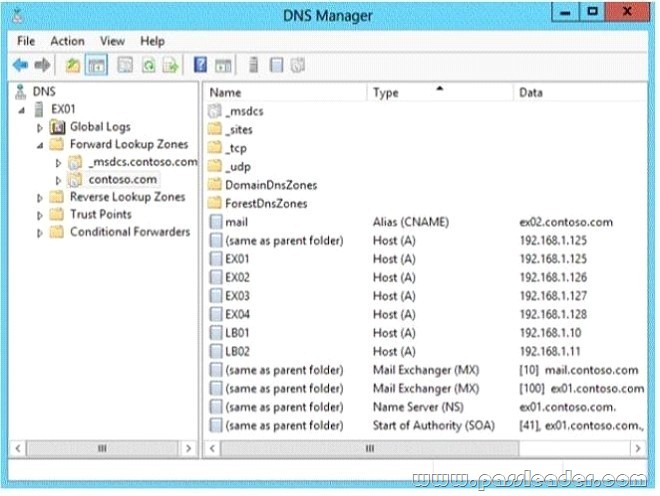
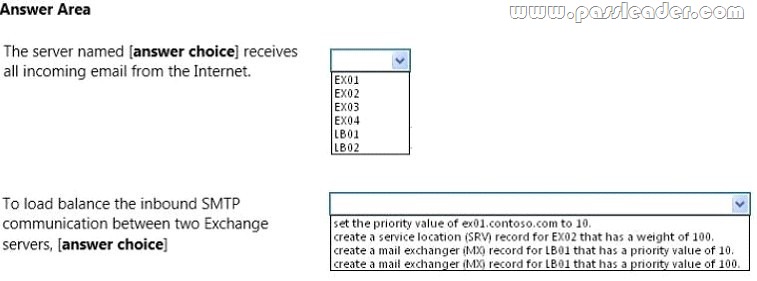
Use the drop-down menus to select the answer choice that completes each statement.
QUESTION 195
Drag and Drop Question
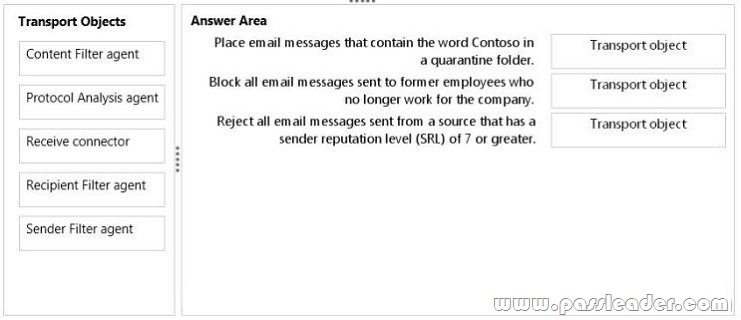
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains a server named EX1. EX1 has the Mailbox server role and the Client Access server role installed. You plan to enable anti-spam protection on EX1. You need to configure the message hygiene settings for email messages received from the Internet. The solution must meet the following requirements:
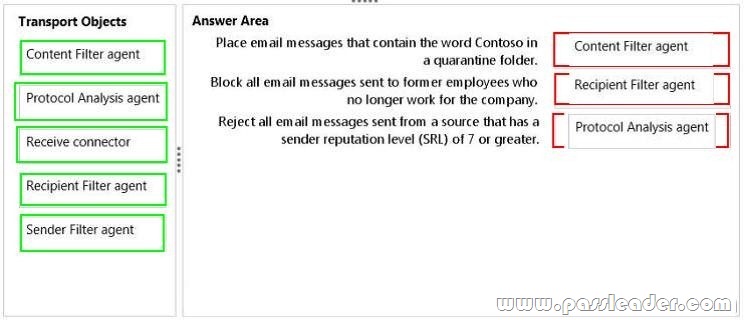
– Place email messages that contain the word Contoso in a quarantine folder.
– Block all email messages sent to former employees who no longer work for the company.
– Reject all email messages sent from a source that has a sender reputation level (SRL) of 7 or greater.
What should you configure? (To answer, drag the appropriate transport objects to the correct requirements. Each object may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.)
QUESTION 196
Your company has offices in New York, Paris, and Montreal. An Active Directory site exists for each office. You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains two servers in each site. One server in each site has the Mailbox server role installed and the other server in each site has the Client Access server role installed. You need to ensure that all of the outbound email from each site is routed through the Client Access server in that site. Which should you do?
A. Remove the Mailbox servers from the list of source servers on each Send connector.
B. Disable the Microsoft Exchange Transport service on each Mailbox server.
C. Run the Set-SendConnector cmdlet and specify the -FrontendProxyEnabted.True parameter.
D. Run the Set-TransportConfig cmdlet and specify the -InternatSMTPServers:$nult parameter.
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://exchangeserverpro.com/exchange-2013-front-end-proxy/
http://blogs.technet.com/b/exchange/archive/2013/01/25/exchange-2013-client-access-server-role.aspx
http://www.msexchange.org/articles-tutorials/exchange-server-2013/planning-architecture/exchange-2013-mail-flow-part3.html
QUESTION 197
You have an Exchange Server 2010 organization. Users access Outlook Web App by using the name mail.contoso.com. You deploy Exchange Server 2013 to the existing organization. You change the DNS record of mail.contoso.com to point to an Exchange Server 2013 Client Access server. The users report that they can no longer access their mailbox from Outlook Web App. The OWA virtual directory in Exchange Server 2010 is configured as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.) You need to ensure that the users on Exchange Server 2010 can access Outlook Web App. Which setting should you change?
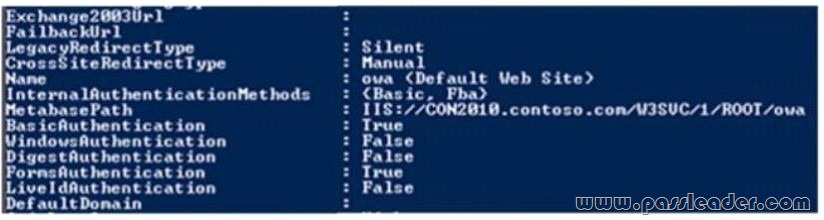
A. WindowsAuthentication
B. FormsAuthentication
C. LegacyRedirectType
D. FailbackUri
Answer: A
Explanation:
Windows Authentication (NTLM) needs to be enabled on the Exchange 2010 Client Access Server to enable the Exchange 2013 Client Access Server to proxy connections.
Exchange Server Deployment Assistant.
Enable and configure Outlook Anywhere.
To allow your Exchange 2013 Client Access server to proxy connections to your Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2010 servers, you must enable and configure Outlook Anywhere on all of the Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2010 servers in your organization. If some Exchange 2007 or Exchange 2010 servers in your organization are already configured to use Outlook Anywhere, their configuration must also be updated to support Exchange 2013. When you use the steps below to configure Outlook Anywhere, the following configuration is set on each Exchange 2007 and Exchange 2010 server: The Outlook Anywhere external URL is set to the external hostname of the Exchange 2013 server. Client authentication, which is used to allow clients like Outlook 2013 to authenticate with Exchange, is set to Basic. Internet Information Services (IIS) authentication, which is used to allow Exchange servers to communicate, set to NTLM and Basic.
QUESTION 198
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains two Mailbox servers and two Client Access servers. You have a database availability group (DAG) that contains both Mailbox servers. You need to deploy public folders. What should you do first?
A. Run the New-PublicFolderDatabase cmdlet and specify the -Server parameter.
B. Run the New-PublicFolder cmdlet and specify the -Path parameter.
C. Run the New-Mailbox cmdlet and specify the -Publicfolder parameter.
D. Run the New-MailboxDatabase cmdlet and specify the -PublicFotderDatabase parameter.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Set Up Public Folders in a New Organization.
New-Mailbox -PublicFolder -Name MasterHierarchy
http://www.msexchange.org/articles-tutorials/exchange-server-2013/migration-deployment/migrating-publicfolders-exchange-2013-part1.html
http://www.msexchange.org/articles-tutorials/exchange-server-2013/migration-deployment/migrating-publicfolders-exchange-2013-part2.html
QUESTION 199
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. You need to install the Hub Transport server role on a new server. You install all the prerequisites for the Hub Transport role on the server. What should you do next?
A. From Windows PowerShell, run the Add-WindowsFeature cmdlet.
B. From Windows PowerShell, run the Install-TransportAgent.ps1 script.
C. At the command prompt, run Setup.com /M:Install /R:HT.
D. At the command prompt, run ServerManagerCmd.exe -IP Exchange-HUB.xml.
Answer: C
QUESTION 200
You have an Exchange Server 2013 server that has the Mailbox, Hub Transport, and Client Access server roles installed. You need to ensure that users can send and receive e-mail by using Windows Live Mail or Microsoft Outlook Express. What should you do on the server?
A. Install and then configure the SMTP server feature.
B. Start the Microsoft Exchange POP3 service and then set the startup type to Automatic.
C. Modify the properties of the MSExchangePOP3 (TCP-in) Windows Firewall rule.
D. Modify the properties of the MSExchangeMailSubmission – RPC (TCP-in) Windows Firewall rule.
Answer: B
Explanation:
By default, pop3 is set to manual.
Get the newest PassLeader 70-341 VCE dumps here: http://www.passleader.com/70-341.html (261 Q&As Dumps –> 272 Q&As Dumps)
And, DOWNLOAD the newest PassLeader 70-341 PDF dumps from Cloud Storage for free: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpfjZ2U1ZfVEZvU0ZreTJkNG1xdmxjS0xUYkdHWVMxWFNRVDhOYTlyRzBjOXM