Valid 70-341 Dumps shared by PassLeader for Helping Passing 70-341 Exam! PassLeader now offer the newest 70-341 VCE dumps and 70-341 PDF dumps, the PassLeader 70-341 exam questions have been updated and ANSWERS have been corrected, get the newest PassLeader 70-341 dumps with VCE and PDF here: http://www.passleader.com/70-341.html (261 Q&As Dumps –> 272 Q&As Dumps)
BTW, DOWNLOAD part of PassLeader 70-341 dumps from Cloud Storage: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpfjZ2U1ZfVEZvU0ZreTJkNG1xdmxjS0xUYkdHWVMxWFNRVDhOYTlyRzBjOXM
QUESTION 101
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains 20 Mailbox servers. You plan to create 10 mailbox databases on each Mailbox server. You need to create a naming convention for all mailbox databases. What should you include in your naming convention?
A. For each mailbox database, provide a database name that is unique within the organization.
B. For each mailbox database, provide a database name that is unique within the Mailbox server.
C. For each mailbox database file, provide a file name that is unique within the organization.
D. For each mailbox database file, provide a file name that is unique within the Mailbox server.
Answer: A
QUESTION 102
You have an Exchange Server organization that contains three servers that have Exchange Server 2013 installed and one server that has Exchange Server 2010 installed. You create the custom RBAC roles shown in the following table. The Seattle help desk manages all of the users in an organizational unit (OU) named Seattle. The Miami help desk manages all of the users in an OU named Miami. The IT Administrators manage all of the users in the forest. You need to recommend which commands must be run to prevent only the members of both help desks from modifying the properties of users who have a department attribute value of Manager. Which three commands should you run? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose three.)

A. new-managementscope “executive users exclusive scope”
-recipientrestrictionfilter { department -eq “manager” } -exclusive sorce
B. new-managementroleassignment -name “managers” -securitygroup “managers”
-role “mail recipients” -exclusiverecipientwritescope “executive users exclusive scope”
C. new-roleassignmentpolicy -name “limited end user policy” -roles “mypersonalinformation”
D. new-rolegroup -name “managers” -roles “mail recipients” -members admins
E. new-rolegroup -name “help desk” -roles “mail recipients” -members admins
Answer: ABD
Explanation:
Note:
– (A) Use the New-ManagementScope cmdlet to create a regular or exclusive management scope. After you create a regular or exclusive scope, you need to associate the scope with a management role assignment. To associate a scope with a role assignment, use the New-ManagementRoleAssignment cmdlet.
– (B) Use the New-ManagementRoleAssignment cmdlet to assign a management role to a management role group, management role assignment policy, user, or universal security group (USG).
QUESTION 103
You have an Exchange Server 2007 organization. You recently deployed a server that has Exchange Server 2013 installed. The Exchange Server organization contains three servers. The servers are configured as shown in the following table. Server2 contains a mailbox for a user named User1. You move the mailbox of User1 to Server3. After the move, User1 fails to access his mailbox by using Outlook Web App. Users who have mailboxes on Server1 and Server2 can access their mailboxes by using Outlook Web Access. You need to ensure that User1 can access his mailbox from the Internet by using Outlook Web App at https://mail.contoso.com. The solution must ensure that users who have mailboxes on Server1 and Server2 can continue to use Outlook Web Access. Which three actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose three.)

A. Export the certificate on Server1 and import the certificate to Server 3.
B. On all of the Exchange servers, install a new certificate that contains the mail.contoso.com and legacy.contoso.com names.
C. Redirect all of the traffic from the Internet for mail.contoso.com to Server3.
D. On all of the Exchange servers, install a new certificate that contains the Server1.contoso.com, server2.contoso.com, server3.contoso.com, and legacy.contoso.com names.
E. Create a host (A) record named legacy.contoso.com that points to Server1.
Answer: ABE
Explanation:
Client Connectivity in an Exchange 2013 Coexistence Environment.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-US/exdeploy2013/Checklist?state=2419-W-FgBEAgAAQACAAIECAQAAAAg~
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-US/exdeploy2013/Checklist?state=2419-W-EQBEAgAAQACAAIECAQAAAAg~
QUESTION 104
You host Exchange Server 2013 organizations for several hundred tenants. The infrastructure contains several custom transport agents. You need to prevent the transport agents from overloading the processors on one of the Exchange servers. Which cmdlet should you run?
A. Set-WorkloadPolicy
B. Set-ResourcePolicy
C. Set-TransportAgent
D. Set-ThrottlingPolicy
Answer: A
QUESTION 105
Drag and Drop Question
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains a server named EX1. You have a user named User1 in the marketing department. You need to prevent User1 from submitting more than 50 email messages per minute to the Exchange Server organization by using Microsoft Outlook. Which three commands should you run? To answer, move the three appropriate commands from the list of commands to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.

Answer:
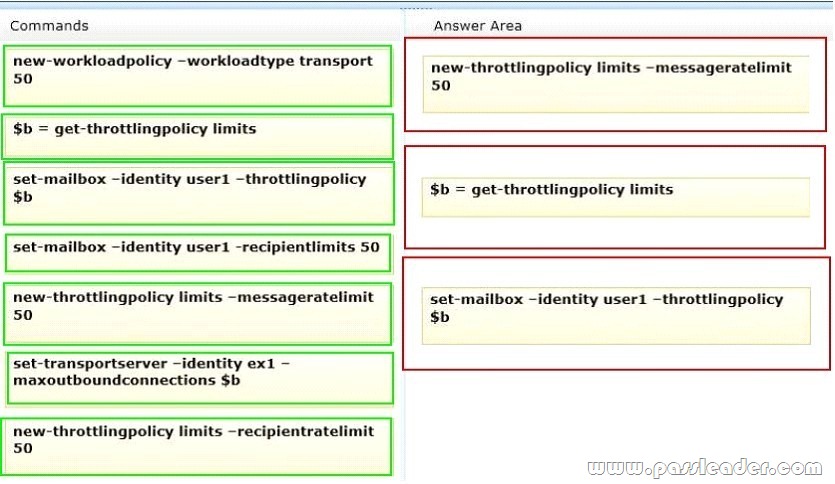
Explanation:
Note:
Box 1:
– Use the New-ThrottlingPolicy cmdlet to create a non-default user throttling policy.
– The MessageRateLimit parameter specifies the number of messages per minute that can be submitted to transport.
Box 3:
– Use the Set-Mailbox cmdlet to modify the settings of an existing mailbox.
You can use this cmdlet for one mailbox at a time.
/ parameter: ThrottlingPolicy
Microsoft.Exchange.Configuration.Tasks.ThrottlingPolicyIdParameter
QUESTION 106
Drag and Drop Question
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains four servers named EX1, EX2, EX3, and EX4. All of the servers are members of a database availability group (DAG) named DAG1. Each server has a copy of a mailbox database named DB1. DB1 has the following characteristics:
– The replay lag time on Ex4 is set to 14 days.
– Single item recovery on all of the servers is set to 14 days.
– None of the servers have Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) backups.
Ex4 has a folder named F:\RDB that is used to store database files during restore operations. Twenty days ago, a user named User1 deleted an email message that had a subject of “Sales Report”. You need to restore the deleted email message to the mailbox of User1. You copy the lagged database and the log files that are older than 20 days to F:\RDB. Which three actions should you perform? To answer, move the three appropriate actions from the list of actions to the answer area and arrange them in the correct order.
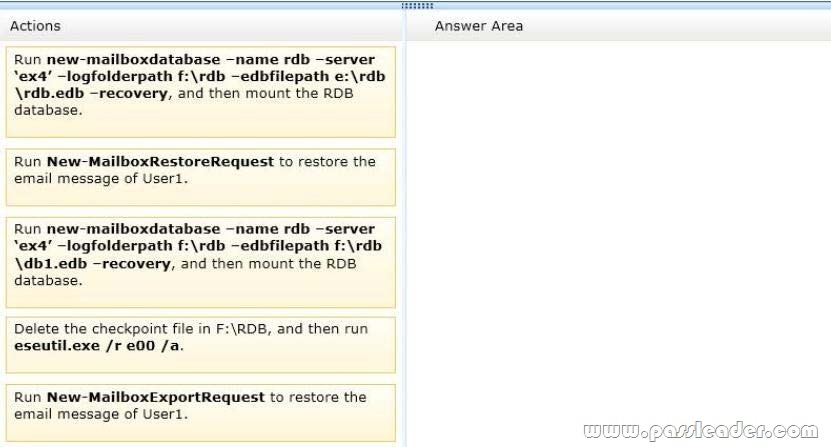
QUESTION 107
Your company has three offices. Each office is configured as an Active Directory site. You have three servers that have Exchange Server 2013 installed named EX1, EX2 and EX3. All three servers have the Client Access server role and the Mailbox server role installed. The Active Directory site links and costs are configured as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.) Site B is designated as a hub site. EX2 fails. You discover that all email messages sent from the users in Site A to the users in Site C are queued on a server in Site A. You need to ensure that the email messages are sent to Site C as quickly as possible. What should you do first?

A. Modify the Active Directory site link costs.
B. Configure Site A as a hub site.
C. Modify the Exchange-specific site link cost.
D. Remove the hub site.
Answer: D
QUESTION 108
Your network contains an internal network and a perimeter network. The internal network contains four offices. The perimeter network is located in a separate office. Each internal office has a direct WAN link to all other internal offices. Each of the four offices that make up the internal network is configured as an Active Directory site. The Active Directory sites and site links are configured as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.) Your company has an Exchange Server 2013 organization. Each site contains two servers that have the Mailbox server role and the Client Access server role installed. To the perimeter network, you deploy two servers that have Exchange Server 2010 Service Pack 2 (SP2) and the Edge Transport server role installed. You configure an Edge Subscription to Site1. You deploy a new email notification application to Site4. The application will send 25,000 email messages daily to external recipients. You need to identify which WAN links will have increased traffic from the new email application. Which WAN link or links should you identify? (Each answer presents part of the solution. Choose all that apply.)
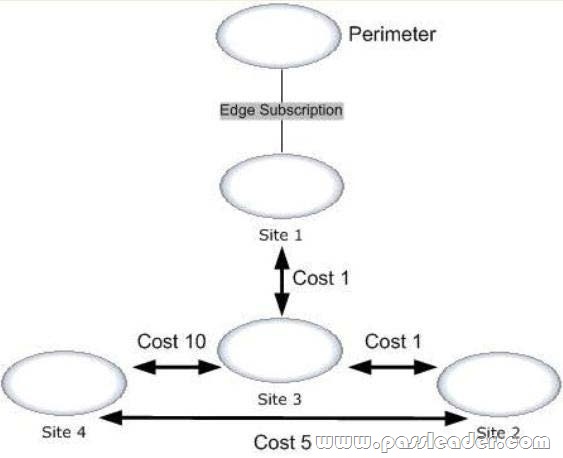
A. The WAN link between Site4 and the perimeter network
B. The WAN link between Site4 and Site3
C. The WAN link between Site1 and the perimeter network
D. The WAN link between Site4 and Site1
E. The WAN link between Site4 and Site2
Answer: CE
Explanation:
C: the traffic will increase on the single WAN link on the perimeter network.
E: The traffic will increase between Site4 and Site2 since the cost of this link (5) plus the cost of the link between Site2 and Site1 (1) is lower the cost on the direct link between Site4 and Site1 (10).
Incorrect answers:
Not A: There is no WAN link between Site4 and the perimeter network.
Not B: The cost of the WAN link between site3 and site3 is high (10). This path will not be chosen.
Not D: There is no WAN link between Site4 and Site1.
QUESTION 109
You have network contoso.com. contoso.com consist of AD DS Domain contoso.com. All Servers running Windows Server 2012 and all Clients running Windows 8 Pro. Server1 runs Mailbox Server Role and Client Access Server Role. You are configuring Anti-Spam Filtering on Server1. You need to ensure that all emails with words “Free Credit Check” are rejected unless the email is sent to Finance Distribution Group. You also need to ensure that all emails from partner company Domain name adatum.com bypass the Anti-Spam Filter. You run the Add-ContentFilterPhrase and add the words “Free Credit Check”. What should you do next?
A. Run the Set-TransportConfig and Set-ContentFilterConfig
B. Run the Set-SenderReputationConfig and Set-TransportConfig
C. Run the Set-ContentFilterConfig and Set-RecipientFilterConfig
D. Run the Set-SenderFilterConfig and Set-RecipientFilterConfig
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-gb/library/bb201691(v=exchg.150).aspx
http://www.jaapwesselius.com/2013/01/10/installing-exchange-server-2013-part-iii/
http://zaliasrobotas.blogspot.co.uk/2013/11/how-to-enable-and-configure-spam-filter.html
http://www.techieshelp.com/exchange-2013-enable-anti-spam/
QUESTION 110
You are evaluating the implementation of a Database Availability Group (DAG). You need to recommend changes to the planned implementation to minimize the loss of large email messages if a single DAG member fails. What should you recommend changing?
A. The preference of the mail exchanger (MX) records
B. The duration of single item recovery
C. The intervals of shadow redundancy
D. The size of the transport dumpster
Answer: C
Explanation:
Shadow redundancy intervals will need to be ammended. SafetyNet is a component of Shadow Redundancy.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd351027(v=exchg.150).aspx
Example 1:
ShadowResubmitTimeSpan on Set-TransportConfig
3 hours
How long a server waits before deciding that a primary server has failed and assumes ownership of shadow messages in the shadow queue for the primary server that’s unreachable.
Example 2:
SafetyNetHoldTime on Set-TransportConfig
2 days
How long successfully processed messages are retained in Safety Net. Unacknowledged shadow messages eventually expire from Safety Net after the sum of SafetyNetHoldTime and MessageExpirationTimeout on Set-TransportService.
QUESTION 111
A user fails to connect to his mailbox by using Outlook Anywhere. The user successfully connects to the mailbox by using an Exchange ActiveSync-enabled mobile device and Outlook Web App. You need to identify what prevents the users from connecting to the mailbox by using Outlook Anywhere. Which tool should you use?
A. Microsoft Outlook Connectivity Test
B. Microsoft Exchange RPC Extractor
C. Microsoft Exchange Server Profile Analyzer
D. Exchange Server MAPI Editor
Answer: A
Explanation:
Outlook Web App.
You can use Outlook Web App to access your Office 365 or other Microsoft Exchange-based email account via a web browser. The URL (web address) you’ll use to sign in to Outlook Web App depends on the type of account you have. Outlook Web App can be used to access any email account that’s hosted on a server that’s running Microsoft Exchange Server 2013.


Mobile devices that are enabled for Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync let users access most of their Microsoft Exchange mailbox data any time, anywhere. There are many different mobile phones and devices enabled for Exchange ActiveSync. These include Windows Phones, Nokia mobile phones, Android phones and tablets, and the Apple iPhone, iPod, and iPad. Although both phone and non-phone mobile devices support Exchange ActiveSync, in most Exchange ActiveSync documentation, we use the term mobile device. Unless the feature or features we’re discussing require a cellular telephone signal, such as SMS message notification, the term mobile device applies to both mobile phones and other mobile devices such as tablets.
EXCHANGE SERVER SETTINGS:

Outlook Anywhere (RPC over HTTP) allows you to use Outlook to connect to your Exchange server from remote locations without first connecting to the VPN. You can also/alternatively, use Outlook Web Access by logging in at https://xmail.bu.edu/ or www.bu.edu/webmail.

For remote connections, Outlook offers Outlook Anywhere, an alternative to VPN connections that allows you to use Outlook just as you normally do at your organization, without the need for any special connections or hardware, such as smart cards and security tokens. Outlook can connect to Exchange through the Internet by using remote procedure call (RPC) over HTTP. The Outlook Anywhere feature allows you to access your Exchange account remotely from the Internet when you are working outside your organization’s firewall.
Test Outlook Anywhere Connectivity.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee633453(v=exchg.150).aspx
Applies to: Exchange Server 2013.
You can test for end-to-end client Outlook Anywhere connectivity by using either the Shell or the Exchange Remote Connectivity Analyzer (ExRCA). This includes testing for connectivity through the Autodiscover service, creating a user profile, and signing in to the user’s mailbox. All the required values are retrieved from the Autodiscover service.
Exchange Remote Connectivity Analyzer (ExRCA).
The Exchange Remote Connectivity Analyzer (ExRCA) is a web-based tool designed to test connectivity with a variety of Exchange protocols. The Microsoft Exchange Remote Connectivity Analyzer (ExRCA) can help you confirm that connectivity for your Exchange servers is configured correctly and diagnose any connectivity issues. The Remote Connectivity Analyzer website offers tests for Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync, Exchange Web Services, Microsoft Outlook, and Internet email.

Use the Shell to test Outlook Anywhere connectivity.
To use the Shell to test Outlook Anywhere connectivity, use the Test-OutlookConnectivity cmdlet.
Run the following command.
Test-OutlookConnectivity -ProbeIdentity ‘OutlookMailboxDeepTestProbe’ -MailboxId
[email protected] -Hostname contoso.com
NOT B
The Microsoft Exchange RPC Extractor is a command-line tool that can parse network captures and interpret remote procedure calls made from a client to Microsoft Exchange Server. RPX uses the information provided in the Microsoft Exchange Server protocol documentation to parse RPCs, remote operations (ROPs), and the parameters for each ROP.
NOT C
The Microsoft Exchange Server Profile Analyzer tool lets administrators collect estimated statistical information from a single mailbox store or across an Exchange Server organization. You can use the collected data to perform the following operations:
– Analyze the performance and health of a mailbox server.
– Improve capacity planning models.
– Improve testing methodologies and tools.
– Improve future client and server products.
NOT D
Use the Microsoft Exchange MAPI Editor to view and modify the contents of a Messaging API (MAPI) store directly.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee633453(v=exchg.150).aspx
QUESTION 112
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. A user named User1 has a mailbox that is enabled for Unified Messaging (UM). User1 has nine call answering rules. When User1 attempts to create a new call answering rule, the user receives an error message. You need to identify what prevents User1 from creating a call answering rule. What should you identify?
A. The mailbox of User1 has the CallAnsweringRulesEnabled parameter set to $false.
B. The UM mailbox policy of User1 has the AllowCallAnsweringRules parameter set to $false.
C. User1 exceeds the Inbox rules storage quota.
D. User1 has the maximum number of call answering rules allowed.
Answer: D
QUESTION 113
Your company has a main office and a branch office. An Active Directory site exits for each office. The offices are connected by a WAN link. You plan to deploy Exchange Server 2013 in each site. You need to identify the number of Exchange servers required to meet the following requirements:
– Maintain user access to mailboxes if a single server fails
– Use the minimize account of Exchange servers in each site
How many servers should you deploy in each site?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer: B
QUESTION 114
Hotspot Question
You need to recommend which script the administrators must run to create the reports required to meet the technical requirements. Which script should you recommend? To answer, select the appropriate script in the answer area.

QUESTION 115
You need to create an exclusion for two helpdesk RBAC (Role Based Access Control) groups to not have access to managers. You will need to pick 3 powershell commands from the available choices.
A. New-ManagementRole, New-ManagementScope,Set-ManagementScope (Guessed)
B. New-ManagementScope, RecipientRestrictionFilter ,New-ManagementRoleAssignment (Guessed)
C. New-ManagementScope, New-ManagementRoleAssignment, CustomRecipientWriteScope (Guessed)
D. Unsure of commands and correct answer
Answer: C
Explanation:
Only chose C as Microsoft recommends that you:
– define the scope,
– then the role,
– then the role group, and finally,
– the role assignment.
However it appears that the custom scope with a recipient filter has to be created in order to filter the scope for the 2 helpdesk role based access groups. The scope, role, and role group assignments are linked by the role assignment itself. Microsoft recommends that you first define the scope, then the role, then the role group, and, finally, the role assignment.

Users assigned the management role. In general, a management role indicates what you can create or modify, and a management role scope indicates where you can create or modify. Regular scopes can be either implicit or explicit scopes, both of which are discussed later in this topic. Exclusive An exclusive scope behaves almost the same as a regular scope. The key difference is that it enables you to deny users access to objects contained within the exclusive scope if those users aren’t assigned a role associated with the exclusive scope. All exclusive scopes are explicit scopes, which are discussed later in this topic. Scopes can be inherited from the management role, specified as a predefined relative scope on a management role assignment, or created using custom filters and added to a management role assignment. Scopes inherited from management roles are called implicit scopes while predefined and custom scopes are called explicit scopes. The following sections describe each type of scope:
– Implicit Scopes
– Explicit Scopes
– Predefined Relative Scopes
– Custom Scopes
– Recipient Filter Scopes
– Configuration Scopes
Each role can have the following types of scopes:
– Recipient read scope
The implicit recipient read scope determines what recipient objects the user assigned the management role is allowed to read from Active Directory.
– Recipient write scope
The implicit recipient write scope determines what recipient objects the user assigned the management role is allowed to modify in Active Directory.
– Configuration read scope
The implicit configuration read scope determines what configuration objects the user assigned the management role is allowed to read from Active Directory.
– Configuration write scope
The implicit configuration write scope determines what organizational, database, and server objects the user assigned the management role is allowed to modify in Active Directory.
Recipient objects include mailboxes, distribution groups, mail enabled users, and other objects. Configuration objects include servers running Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, and databases located on servers running Exchange. Each type of scope can be either an implicit scope or explicit scope.
Role Based Access Control Groups.
Role Based Access Control (RBAC) is the permissions model used in Microsoft Exchange Server 2013. With RBAC, you don’t need to modify and manage access control lists (ACLs), which was done in Exchange Server 2007. ACLs created several challenges in Exchange 2007, such as modifying ACLs without causing unintended consequences, maintaining ACL modifications through upgrades, and troubleshooting problems that occurred due to using ACLs in a nonstandard way. RBAC enables you to control, at both broad and granular levels, what administrators and end-users can do. RBAC also enables you to more closely align the roles you assign users and administrators to the actual roles they hold within your organization. In Exchange 2007, the server permissions model applied only to the administrators who managed the Exchange 2007 infrastructure. In Exchange 2013, RBAC now controls both the administrative tasks that can be performed and the extent to which users can now administer their own mailbox and distribution groups. RBAC has two primary ways of assigning permissions to users in your organization, depending on whether the user is an administrator or specialist user, or an end-user management role groups and management role assignment policies. Each method associates users with the permissions they need to perform their jobs. A third, more advanced method, direct user role assignment, can also be used:

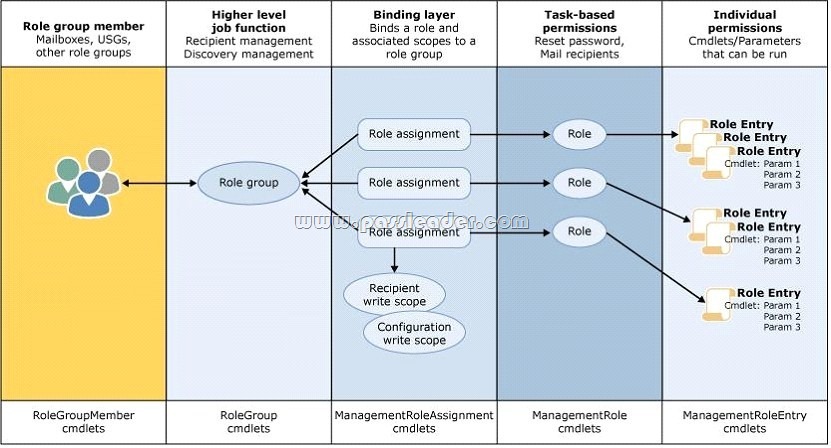
Built-in Role Groups.
Microsoft Exchange Server 2013 includes several management role groups by default. The following built-in role groups provide you with a preconfigured set of roles that you can assign to various administrator and specialist users in your organization:
– Organization Management
– View-Only Organization Management
– Recipient Management
– UM Management
– Help Desk
– Hygiene Management
– Compliance Management
– Records Management
– Discovery Management
– Public Folder Management
– Server Management
– Delegated Setup
New-ManagementScope (Example).
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd335137(v=exchg.150).aspx
EXAMPLE 4
This example creates the Protected Exec Users exclusive scope. Users that contain the string “VP” in their title match the recipient filter for the scope. When the exclusive scope is created, all users are immediately blocked from modifying the recipients that match the exclusive scope until the scope is associated with a management role assignment. If other role assignments are associated with other exclusive scopes that match the same recipients, those assignments can still modify the recipients.
New-ManagementScope -Name “Protected Exec Users” -RecipientRestrictionFilter { Title -Like “*VP*” } -Exclusive
New-ManagementRoleAssignment.
The exclusive scope is then associated with a management role assignment that assigns the Mail Recipients management role to the Executive Administrators role group. This role group contains administrators who are allowed to modify the mailboxes of high-profile executives. Only the administrators of the Executive Administrators role group can modify users with the string “VP” in their title.
New-ManagementRoleAssignment -SecurityGroup “Executive Administrators” -Role “Mail Recipients” -CustomRecipientWriteScope “Protected Exec Users”
This example assigns the Eng Help Desk role to the Eng HD Personnel role group. The assignment restricts the recipient write scope of the role to the contoso.com/Engineering/Users OU. Users who are members of the Eng HD Personnel role group can only create, modify, or remove objects contained within that OU.
New-ManagementRoleAssignment -Role “Eng Help Desk” -SecurityGroup “Eng HD Personnel” –RecipientOrganizationalUnitScope contoso.com/Engineering/Users
New-ManagementRole.
Use the New-ManagementRole cmdlet to create a management role based on an existing role or create an unscoped management role.
EXAMPLE 1
This example creates the management role Redmond Journaling View-Only based on the Journaling parent role.
New-ManagementRole -Name “Redmond Journaling View-Only” -Parent Journaling
New-RoleGroup.
Use the New-RoleGroup cmdlet to create a management role group on a server running Microsoft Exchange Server 2013.
EXAMPLE 1
This example creates a role group. The Mail Recipients and Mail Enabled Public Folders roles are assigned to the role group, and the users Kim and Martin are added as members. Because no scopes were provided, Kim and Martin can manage any recipient and reset passwords for any users in the organization.
New-RoleGroup -Name “Limited Recipient Management” -Roles “Mail Recipients”, “Mail Enabled Public Folders” -Members Kim, Martin
Look here:
Understanding Management Role Scopes.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd335146(v=exchg.150).aspx
As we need to set deny access we want to set explicit recipcient filter scope for the existing helpdesk group, removing the managers from the scope. Then create a new RBAC group and implicit scope the managers mailboxes. So my guess would be something like:
New-ManagementRole -Name “Management role for CEO”
New-ManagementScope -Name “Management Scope for CEO” -RecipientRestrictionFilter { Title -Like “*CEO*” } -Exclusive
Set-ManagementScope “Helpdesk Users” -RecipientRestrictionFilter { Company -eq ‘Contoso users’ -and Function -like ‘CEO’
As we do not know what RBAC setup already exists, this kind of smells like Microsoft, but hey this is a start.
QUESTION 116
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains five servers. Your company has a finance department, a marketing department, and a research department. Users in the marketing department are prevented from creating more than two Exchange ActiveSync device associations. You have a user named User5 in the finance department. You need to prevent User5 from creating more than two Exchange ActiveSync device associations. Which cmdlet should you use?
A. Set-ThrottlingPolicyAssociation
B. Set-ResourcePolicy
C. Set-ActiveSyncMailboxPolicy
D. Set-CASMailbox
Answer: A
Explanation:
Set-ThrottlingPolicyAssociation: Exchange 2013 Help
Set-ThrottlingPolicy: Exchange 2013 Help
QUESTION 117
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization named for Contoso. A user named Admin1 is a member of the Domain Admins group. Admin1 fails to synchronize a new Windows Phone device by using Exchange ActiveSync and receives an HTTP 500 error message. Admin1 successfully logs on to Outlook Web App and Outlook Anywhere. You need to ensure that Admin1 can synchronize the new Windows Phone device by using Exchange ActiveSync. What should you do?
A. Install a trusted root certificate on the Windows Phone device.
B. Create a new mobile device mailbox policy.
C. Enable permission inheritance on the Admin1 user account.
D. Disable permission inheritance on the Admin1 user account.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Mobile device mailbox policy.
In Microsoft Exchange Server 2013, you can create mobile device mailbox policies to apply a common set of policies or security settings to a collection of users. After you deploy Exchange ActiveSync in your Exchange 2013 organization, you can create new mobile device mailbox policies or modify existing policies. When you install Exchange 2013, a default mobile device mailbox policy is created. All users are automatically assigned this default mobile device mailbox policy.
NOT A
It is possible to save a digital certificate to a file and install a digital certificate on a Windows Mobile phone. Microsoft Exchange ActiveSync enables a variety of mobile phones to synchronize with an Exchange mailbox. A digital certificate might need to be installed on a user’s mobile phone if Exchange ActiveSync is required to use Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and your organization uses a certificate that isn’t from a trusted commercial certification authority (CA). No mention of SSL in this question.
NOT B
This is a permission inheritance issue.
NOT D
Need to enable permission inheritance not disable it or leave it as disabled.
C

QUESTION 118
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization that contains a server named EX1. Your network contains a non-critical internal application that regularly connects to the POP3 Service on EX1. Users report that Outlook Web App performs more slowly than usual. You discover that EX1 frequently has a CPU utilization that is greater than 85 percent. You need to configure EX1 temporarily to allocate more processor resources to Outlook Web App and to allocate less processor resources to POP3. Which two new policies should you create? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
A. a throttling policy that sets OWAMaxConcurrency to 25
B. a workload policy for POP3 that sets the WorkloadClassification to Discretionary
C. a workload policy for Outlook Web App that sets the WorkloadClassification to Discretionary
D. a throttling policy that sets PopMaxConcurrency to 25
E. a workload policy for POP3 that sets the WorkloadClassification to CustomerExpectation
F. a workload policy for Outlook Web App that sets the WorkloadClassification to CustomerExpectation
Answer: BF
Explanation:
A workload policy.
An Exchange workload is an Exchange Server feature, protocol, or service that’s been explicitly defined for the purposes of Exchange system resource management. Each Exchange workload consumes system resources such as CPU, mailbox database operations, or Active Directory requests to run user requests or background work. Examples of Exchange workloads include Outlook Web App, Exchange ActiveSync, mailbox migration, and mailbox assistants.
There are two ways to manage Exchange workloads: by monitoring the health of system resources or by controlling how resources are consumed by individual users (sometimes called user throttling in Exchange 2010). Managing workloads based on the health of system resources is new in Microsoft Exchange Server 2013. Controlling how resources are consumed by individual users was possible in Exchange Server 2010, and this capability has been expanded for Exchange Server 2013. You can customize the workload management settings if you want to change the default behavior of the feature for the needs of your environment.
Workload classifications.
Each Exchange workload (for example, the Calendar Synchronization Assistant workload), is assigned a classification. Workload policy settings are used to group each workload into a class. Classification is used to control both priority and target resource usage. Exchange workloads can be assigned one of the following classifications:
– Urgent
– Customer Expectation
– Internal Maintenance
– Discretionary
Workloads in a higher classification group are given preference as resource health shows signs of degrading. For example, when a resource such as local server CPU reaches high usage, workloads classified as Internal. Maintenance may continue to run, while workloads classified as Discretionary may be stopped.
NOT AD
A throttling policy is related to Exchange 2010.
NOT C
Do not need to allocate less priority to Outlook Web App, but more.
NOT E
POP3 is allocated too much resources with a WorkloadClassification of CustomerExpectation.
B
Need to allocate less priority to POP3.
F
Outlook Web App is allocated the appropriate amount of resources with a WorkloadClassification of CustomerExpectation.
QUESTION 119
Hotspot Question
Your company has an Exchange Server 2013 organization. The company hires 200 temporary employees. You create a mailbox for each temporary employee. You create a new management role named CustomBaseOptions that uses MyBaseOptions as a parent. You create a new management role named CustomContactlnfo that uses MyContactlnfo as a parent. You plan to apply the new management roles to the temporary employees. You need to identify which management roles must be modified to prevent the temporary employees from performing the following task:
– Adding a user photo
– Viewing delivery reports
– Viewing the Install Apps feature
– Changing the value of the office location
Which management roles should you identify? To answer, select the appropriate management role for each task in the answer area.

Answer:

Explanation:
https://msundis.wordpress.com/tag/rbac/
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd876850(v=exchg.150).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd876910(v=exchg.150).aspx
http://www.exchange-genie.com/2009/08/owa-exchange-control-panel-ecp-part1-rbac/
http://www.proexchange.be/blogs/exchange2010/archive/2011/01/11/restricting-access-to-exchange-control-panel-for-users.aspx
QUESTION 120
You have an Exchange Server 2013 organization. You are troubleshooting an email delivery problem. You need to disable temporarily the antimalware scanning on a server that has Exchange Server 2013 installed. The solution must ensure that the antimalware engine continues to download updates. What should you run?
A. the Set-TransportConfig cmdlet
B. the Disable-Antimalwarescanning.psl script
C. the New-MalwareFilterPolicy cmdlet
D. the Set-MalwareFilteringServer cmdlet
Answer: D
Explanation:
Disable or Bypass Anti-Malware Scanning.
Important:
Bypassing malware filtering should only be done when troubleshooting a problem. You should restore malware filtering after you have finished troubleshooting. To temporarily bypass malware filtering, run the following command:
Set-MalwareFilteringServer <ServerIdentity> -BypassFiltering $true
To restore malware filtering, run the following command:
Set-MalwareFilteringServer <ServerIdentity> -BypassFiltering $false
Get the newest PassLeader 70-341 VCE dumps here: http://www.passleader.com/70-341.html (261 Q&As Dumps –> 272 Q&As Dumps)
And, DOWNLOAD the newest PassLeader 70-341 PDF dumps from Cloud Storage for free: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpfjZ2U1ZfVEZvU0ZreTJkNG1xdmxjS0xUYkdHWVMxWFNRVDhOYTlyRzBjOXM

