Valid 70-410 Dumps shared by PassLeader for Helping Passing 70-410 Exam! PassLeader now offer the newest 70-410 VCE dumps and 70-410 PDF dumps, the PassLeader 70-410 exam questions have been updated and ANSWERS have been corrected, get the newest PassLeader 70-410 dumps with VCE and PDF here: http://www.passleader.com/70-410.html (512 Q&As Dumps –> 528 Q&As Dumps)
BTW, DOWNLOAD part of PassLeader 70-410 dumps from Cloud Storage: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpfnJzOE1fWnlJOWVtaE93SnJNT3gtaTNYYnVpZkw5THBSMWRKbFlfaXh1azg
QUESTION 121
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has following storage spaces:
– Data
– Users
– Backups
– Primordial
You add an additional hard disk to Server1. You need to identify which storage space contains the new hard disk. Which storage space contains the new disk?
A. Data
B. Primordial
C. Users
D. Backups
Answer: B
Explanation:
http://blogs.technet.com/b/canitpro/archive/2012/12/13/storage-pools-dive-right-in.aspx
http://blogs.technet.com/b/askpfeplat/archive/2012/10/10/windows-server-2012-storagespaces-is-it-for-youcould-be.aspx
QUESTION 122
You have a server named Server1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2 and has the File and Storage Services server role installed. You attach four 500-GB disks to Server1. You need to configure the storage to meet the following requirements:
– Storage for an application named Application1 must be provided. Application1 requires 20 GB and will require a maximum of 800 GB in three years.
– Storage for an application named Application2 must be provided. Application2 requires 20 GB and will require a maximum of 900 GB in three years.
– The solution must provide the ability to dynamically add storage without requiring configuration changes to the applications.
– The storage must be available if a single disk fails.
Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
A. From File and Storage Services, create virtual disks by using fixed provisioning.
B. From File and Storage Services, create a storage pool that uses all four disks.
C. From Disk Management, create two new mirror volumes that use two disks each.
D. From Disk Management, create a new RAID-5 volume that uses all four disks.
E. From File and Storage Services, create virtual disks by using thin provisioning.
Answer: BE
Explanation:
Original answer is AB. But the correct answer is B and E. it can’t be A, because a fixed disk can’t get expanding.
QUESTION 123
Your network contains multiple subnets. On one of the subnets, you deploy a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. You install the DNS Server server role on Server1, and then you create a standard primary zone named contoso.com. You need to ensure that client computers can resolve single-label names to IP addresses. What should you do first?
A. Create a reverse lookup zone.
B. Convert the contoso.com zone to an Active Directory-integrated zone.
C. Configure dynamic updates for contoso.com.
D. Create a GlobalNames zone.
Answer: A
Explanation:
names to IP Addresses = Forward Lookup Zone
IP Addresses to names = Reverse Lookup Zone
QUESTION 124
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has six network adapters. Two of the network adapters are connected to a network named LAN1, two of the network adapters are connected to a network named LAN2, and two of the network adapters are connected to a network named LAN3. You create a network adapter team named Team1 from the two adapters connected to LAN1. You create a network adapter team named Team2 from the two adapters connected to LAN2. A company policy states that all server IP addresses must be assigned by using a reserved address in DHCP. You need to identify how many DHCP reservations you must create for Server1. How many reservations should you identify?
A. 3
B. 4
C. 6
D. 8
Answer: B
Explanation:
2 Adapters = LAN1 = Team1 = 1 IP
2 Adapters = LAN2 = Team2 = 1 IP
2 Adapters = LAN3 = No Team = 2 IP
1 + 1 + 2 = 4
QUESTION 125
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. All servers run Windows Server 2012 R2. The domain contains a server named Server1. You open Review Options in the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard, and then you click View script. You need to ensure that you can use the script to promote Server1 to a domain controller. Which file extension should you use to save the script?
A. .ps1
B. .bat
C. .xml
D. .cmd
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831457.aspx
The Review Options page in Server Manager also offers an optional View Script button to create a Unicode text file that contains the current ADDS Deployment configuration as a single Windows PowerShell script. This enables you to use the Server Manager graphical interface as a Windows PowerShell deployment studio. Use the Active Directory Domain Services Configuration Wizard to configure options, export the configuration, and then cancel the wizard. This process creates a valid and syntactically correct sample for further modification or direct use.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc764242.aspx
Windows PowerShell scripts should have one of the following extensions:

QUESTION 126
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a server named Server!. Server1 runs a Server Core installation of Windows Server 2012 R2. You install the DNS Server server role on Server1. You need to perform the following configurations on Server1:
– Create an Active Directory-integrated zone named adatum.com.
– Send unresolved DNS client queries for other domain suffixes to the DNS server of your company’s Internet Service Provider (ISP).
Which Windows PowerShell cmdlets should you use? To answer, drag the appropriate cmdlet to the correct configuration in the answer area. Each cmdlet may be used once, more than once, or not at all. You may need to drag the split bar between panes or scroll to view content.

Answer:

Explanation:
Add-DnsServerDirectoryPartition: Creates a DNS application directory partition.
Add-DnsServerPrimaryZone: Adds a primary zone to a DNS server.
Set-DNSServer: Overwrites a DNS server configuration.
Set-DNSServerForwarder: Changes forwarder settings on a DNS server.
Set-DNSServerDSSetting: Modifies DNS Active Directory settings.
Set-DNSServerSetting: Modifies DNS server settings.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj649942(v=wps.620).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj649876(v=wps.620).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj649845(v=wps.620).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj649887(v=wps.620).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj649874.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj649909.aspx
QUESTION 127
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The network contains 500 client computers that run Windows 8. All of the client computers connect to the Internet by using a web proxy. You deploy a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has the DNS Server server role installed. You configure all of the client computers to use Server1 as their primary DNS server. You need to prevent Server1 from attempting to resolve Internet host names for the client computers. What should you do on Server1?
A. Create a primary zone named “.”.
B. Configure the Security settings of the contoso.com zone.
C. Create a zone delegation for GlobalNames.contoso.com.
D. Create a stub zone named “root”.
Answer: A
Explanation:
When you install DNS on a Windows server that does not have a connection to the Internet, the zone for the domain is created and a root zone, also known as a dot zone, is also created. This root zone may prevent access to the Internet for DNS and for clients of the DNS. If there is a root zone, there are no other zones other than those that are listed with DNS, and you cannot configure forwarders or root hint servers.
Root Domain
This is the top of the tree, representing an unnamed level; it is sometimes shown as two empty quotation marks (“”), indicating a null value. When used in a DNS domain name, it is stated by a trailing period (.) to designate that the name is located at the root or highest level of the domain hierarchy. In this instance, the DNS domain name is considered to be complete and points to an exact location in the tree of names. Names stated this way are called fully qualified domain names (FQDNs).
DNS Domain Name Hierarchy:

QUESTION 128
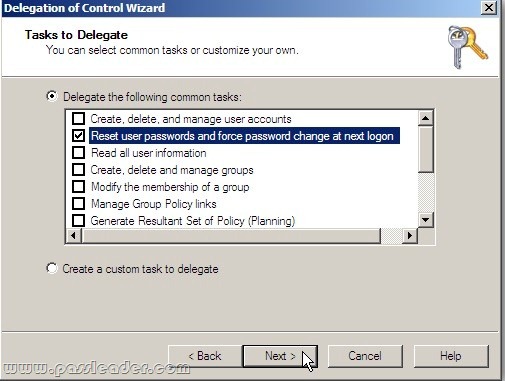
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains 100 user accounts that reside in an organizational unit (OU) named OU1. You need to ensure that a user named User1 can link and unlink Group Policy Objects (GPOs) to OU1. The solution must minimize the number of permissions assigned to User1. What should you do?
A. Modify the permissions on OU1.
B. Run the Set-GPPermission cmdlet.
C. Add User1 to the Group Policy Creator Owners group.
D. Modify the permissions on the User1 account.
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://www.howtogeek.com/50166/using-the-delegation-of-control-wizard-to-assign-permissions-in-server-2008/
QUESTION 129
You have a server that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. The server contains the disks configured as shown in the following table.

You need to create a volume that can store up to 3 TB of user files. The solution must ensure that the user files are available if one of the disks in the volume fails. What should you create?
A. a mirrored volume on Disk 1 and Disk 4
B. a mirrored volume on Disk 2 and Disk 3
C. a RAID-5 volume on Disk 1, Disk 2, and Disk 3
D. a spanned volume on Disk 0 and Disk 4
Answer: B
Explanation:
A mirrored volume provides an identical twin of the selected volume. All data written to the mirrored volume is written to both volumes, which results in disk capacity of only 50 percent. Any volume can be mirrored, including the system and boot volumes. The disk that you select for the shadow volume does not need to be identical to the original disk in size, or in its number of tracks and cylinders. This means that you do not have to replace a failed disk with an identical model. The unused area that you select for the shadow volume cannot be smaller than the original volume. If the area that you select for the shadow volume is larger than the original, the extra space on the shadow disk can be configured as another volume. Dynamic disks provide features that basic disks do not, such as the ability to create volumes that span multiple disks (spanned and striped volumes) and the ability to create fault-tolerant volumes (mirrored and RAID-5 volumes). The following operations can be performed only on dynamic disks:
– Create and delete simple, spanned, striped, mirrored, and RAID-5 volumes.
– Extend a simple or spanned volume.
– Remove a mirror from a mirrored volume or break the mirrored volume into two volumes.
– Repair mirrored or RAID-5 volumes.
– Reactivate a missing or offline disk.
You need at least two dynamic disks to create a mirrored volume. Mirrored volumes are fault tolerant and use RAID-1, which provides redundancy by creating two identical copies of a volume. Mirrored volumes cannot be extended. Both copies (mirrors) of the mirrored volume share the same drive letter.

http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc779765%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa363785%28v=vs.85%29.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc938487.aspx
QUESTION 130
What should you do for server core so it can be managed from another server 2012 R2?
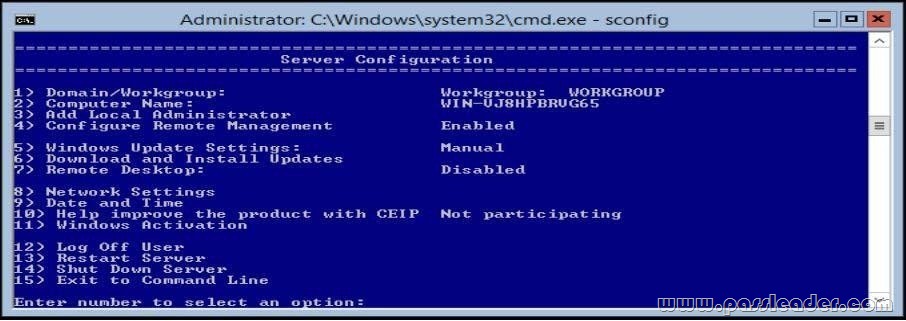
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
E. 5
F. 6
G. 7
H. 8
I. 9
J. 10
K. 11
L. 12
M. 13
N. 14
O. 15
Answer: H
Explanation:
4) Configure Remote Management is already “Enabled”.
8) Network Settings. You can configure the IP address to be assigned automatically by a DHCP Server or you can assign a static IP address manually. This option allows you to configure DNS Server settings for the server as well.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj647766.aspx
QUESTION 131
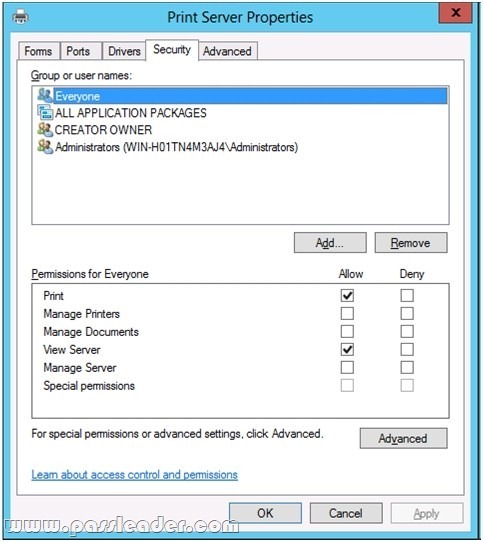
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a server named Server1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2. On Server1, you create a printer named Printer1. You share Printer1 and publish Printer1 in Active Directory. You need to provide a group named Group1 with the ability to manage Printer1. What should you do?
A. From Print Management, configure the Sharing settings of Printer1.
B. From Active Directory Users and Computers, configure the Security settings of Server1-Printer1.
C. From Print Management, configure the Security settings of Printer1.
D. From Print Management, configure the Advanced settings of Printer1.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Reference:
Set Permissions for Print Servers.
Open Print Management. In the left pane, click Print Servers, right-click the Applicable print server and then click Properties. On the Securitytab, under group or users names, click a user or group for which you want to set permissions. Under Permissions for <user or group name>, select the Allow or Deny check boxes for the permissions listed as needed. To edit Special permissions, click Advanced. On the Permissions tab, click a user group, and then click Edit. In the Permission Entrydialog box, select the Allow or Deny check boxes for the permissions that you want to edit.
QUESTION 132
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. All servers run Windows Server 2012 R2. Client computers run either Windows 7 or Windows 8. All of the computer accounts of the client computers reside in an organizational unit (OU) named Clients. A Group Policy Object (GPO) named GP01 is linked to the Clients OU. All of the client computers use a DNS server named Server1. You configure a server named Server2 as an ISATAP router. You add a host (A) record for ISATAP to the contoso.com DNS zone. You need to ensure that the client computers locate the ISATAP router. What should you do?
A. Run the Add-DnsServerResourceRecord cmdlet on Server1.
B. Configure the DNS Client Group Policy setting of GPO1.
C. Configure the Network Options Group Policy preference of GPO1.
D. Run the Set-DnsServerGlobalQueryBlockList cmdlet on Server1.
Answer: D
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj649857(v=wps.620).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc794902%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/security/bulletin/ms09-008
http://www.cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2009-0093
QUESTION 133
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2 and has the Remote Access server role installed. A user named User1 must connect to the network remotely. The client computer of User1 requires Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) for remote connections. CHAP is enabled on Server1. You need to ensure that User1 can connect to Server1 and authenticate to the domain. What should you do from Active Directory Users and Computers?
A. From the properties of Server1, select Trust this computer for delegation to any service (Kerberos only).
B. From the properties of Server1, assign the Allowed to Authenticate permission to User1.
C. From the properties of User1, select Use Kerberos DES encryption types for this account.
D. From the properties of User1, select Store password using reversible encryption.
Answer: D
Explanation:
The Store password using reversible encryption policy setting provides support for Applications that use protocols that require the user’s password for authentication. Storing encrypted passwords in a way that is reversible means that the encrypted passwords can be decrypted. A knowledgeable attacker who is able to break this encryption can then log on to network resources by using the compromised account. For this reason, never enable Store password using reversible encryption for all users in the domain unless Application requirements outweigh the need to protect password information. If you use the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) through remote access or Internet Authentication Services (IAS), you must enable this policy setting. CHAP is an authentication protocol that is used by remote access and network connections. Digest Authentication in Internet Information Services(IIS) also requires that you enable this policy setting. If your organization uses CHAP through remote access or IAS, or Digest Authentication in IIS, you must configure this policy setting to Enabled. This presents a security risk when you Apply the setting through Group Policy on a user-by-user basis because it requires the appropriate user account object to be opened in Active Directory Users and Computers.

http://technet.microsoft.com/pt-pt/library/hh994559%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 134
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has the Hyper-V server role installed. Server1 has a virtual switch named RDS Virtual. You replace all of the network adapters on Server1 with new network adapters that support single-root I/O visualization (SR-IOV). You need to enable SR-IOV for all of the virtual machines on Server1. Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
A. On each virtual machine, modify the Advanced Features settings of the network adapter.
B. Modify the settings of the RDS Virtual virtual switch.
C. On each virtual machine, modify the BIOS settings.
D. Delete, and then recreate the RDS Virtual virtual switch.
E. On each virtual machine, modify the Hardware Acceleration settings of the network adapter.
Answer: DE
Explanation:
D: The first step when allowing a virtual machine to have connectivity to a physical network is to create an external virtual switch using Virtual Switch Manager in Hyper-V Manager. The additional step that is necessary when using SR-IOV is to ensure the check box is checked when the virtual switch is being created. It is not possible to change a “non SR-IOV mode” external virtual switch into an “SR-IOV mode” switch. The choice must be made a switch creation time.
E: Once a virtual switch has been created, the next step is to configure a virtual machine. SR-IOV in Windows Server “8” is supported on x64 editions of Windows “8” as a guest operating system (as in Windows “8” Server, and Windows “8” client x64, but not x86 client). We have rearranged the settings for a virtual machine to introduce sub-nodes under a network adapter, one of which is the hardware acceleration node. At the bottom is a checkbox to enable SR-IOV.
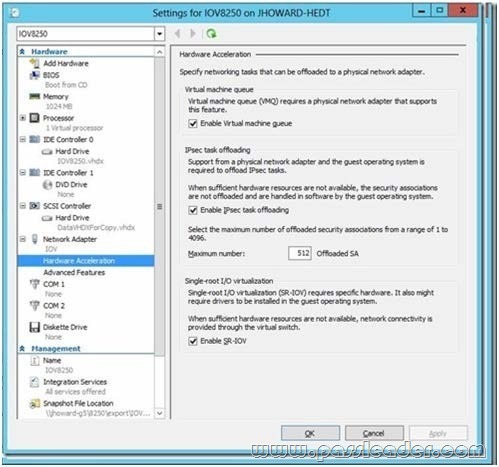
Note:
* Steps:
– SR-IOV must be enabled on virtual switch
– Install additional network drivers in the guest OS
– Enable SR-IOV within the VMs though Hyper-V Manager
* Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) is a standard introduced by the PCI-SIG that owns and manages PCI specifications as open industry standards. SR-IOV enables network traffic to bypass the software switch layer of the Hyper-V Virtualization stack to reduce the I/O overhead in this layer. It allows an SR-IOV virtual function of a physical network adapter to be assigned directly to a virtual machine to increase network through put by reducing latency. Host CPU overhead also get reduced for processing network traffic.
* The diagram below illustrates how SR-IOV allows virtual machines to directly address the physical NIC.
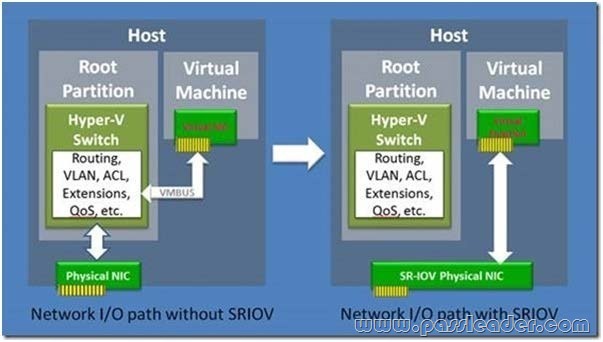
Reference: Everything you wanted to know about SR-IOV in Hyper-V (Part 5)
QUESTION 135
Your network contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 is a member of a workgroup. You need to configure a local Group Policy on Server1 that will apply only to non- administrators. Which tool should you use?
A. Server Manager
B. Group Policy Management Editor
C. Group Policy Management
D. Group Policy Object Editor
Answer: D
Explanation:

http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc766291%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 136
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a server named Server! that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 contains a virtual machine named VM1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. You need to ensure that a user named User1 can install Windows features on VM1. The solution must minimize the number of permissions assigned to User1. To which group should you add User1?
A. Administrators on VM1
B. Power Users on VM1
C. Hyper-V Administrators on Server1
D. Server Operators on Server1
Answer: A
Explanation:
In Windows Server 2012 R2, the Server Manager console and Windows PowerShell-cmdlets for Server Manager allow installation of roles and features to local or remote servers, or offline virtual hard disks (VHDs). You can install multiple roles and features on a single remote server or offline VHD in a single Add Roles and Features Wizard or Windows PowerShell session. You must be logged on to a server as an administrator to install or uninstall roles, role services, and features. If you are logged on to the local computer with an account that does not have administrator rights on your target server, right-click the target server in the Servers tile, and then click Manage As to provide an account that has administrator rights. The server on which you want to mount an offline VHD must be added to Server Manager, and you must have Administrator rights on that server.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831809.aspx
QUESTION 137
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named adatum.com. The domain contains a member server named LON-DC1. LON-DC1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2 and has the DHCP Server server role installed. The network contains 100 client computers and 50 IP phones. The computers and the phones are from the same vendor. You create an IPv4 scope that contains addresses from 172.16.0.1 to 172.16.1.254. You need to ensure that the IP phones receive IP addresses in the range of 172.16.1.100 to 172.16.1.200. The solution must minimize administrative effort. What should you create?
A. Server level policies
B. Filters
C. Reservations
D. Scope level policies
Answer: D
Explanation:
When a client matches the conditions of a policy, the DHCP server responds to the clients based on the settings of a policy. Settings associated to a policy can be an IP address range and/or options. An administrator could configure the policy to provide an IP address from a specified sub-range within the overall IP address range of the scope. You can also provide different option values for clients satisfying this policy. Policies can be defined server wide or for a specific scope. A server wide policy – on the same lines as server wide option values – is applicable to all scopes on the DHCP server. A server wide policy however cannot have an IP address range associated with it. There a couple of ways to segregate clients based on the type of device. One way to do this is by using vendor class/identifier. This string sent in option 60 by most DHCP clients identify the vendor and thereby the type of the device. Another way to segregate clients based on device type is by using the MAC address prefix. The first three bytes of a MAC address is called OUI and identify the vendor or manufacturer of the device. By creating DHCP policies with conditions based on Vendor Class or MAC address prefix, you can now segregate the clients in your subnet in such a way, that devices of a specific type get an IP address only from a specified IP address range within the scope. You can also give different set of options to these clients. In conclusion, DHCP policies in Windows Server 2012 R2 enables grouping of clients/devices using the different criteria and delivering targeted network configuration to them. Policy based assignment in Windows Server 2012 R2 DHCP allows you to create simple yet powerful rules to administer DHCP on your network.


QUESTION 138
Your network contains an Active Directory forest. The forest contains a single domain named contoso.com. The domain contains four domain controllers. The domain controllers are configured as shown in the following table.
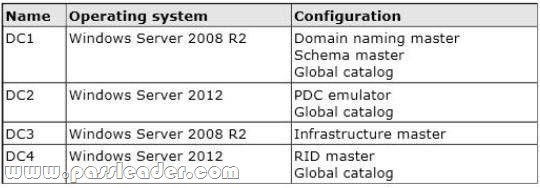
You plan to deploy a new domain controller named DC5 in the contoso.com domain. You need to identify which domain controller must be online to ensure that DC5 can be promoted successfully to a domain controller. Which domain controller should you identify?
A. DC1
B. DC2
C. DC3
D. DC4
Answer: D
Explanation:
Relative ID (RID) Master:
Allocates active and standby RID pools to replica domain controllers in the same domain. (corp.contoso.com) Must be online for newly promoted domain controllers to obtain a local RID pool that is required to advertise or when existing domain controllers have to update their current or standby RID pool allocation. The RID master is responsible for processing RID pool requests from all domain controllers in a particular domain. When a DC creates a security principal object such as a user or group, it attaches a unique Security ID (SID) to the object. This SID consists of a domain SID (the same for all SIDs created in a domain), and a relative ID (RID) that is unique for each security principal SID created in a domain. Each DC in a domain is allocated a pool of RIDs that it is allowed to assign to the security principals it creates. When a DC’s allocated RID pool falls below a threshold, that DC issues a request for additional RIDs to the domain’s RID master. The domain RID master responds to the request by retrieving RIDs from the domain’s unallocated RID pool and assigns them to the pool of the requesting DC At any one time, there can be only one domain controller acting as the RID master in the domain.

The Infrastructure Master – the purpose of this role is to ensure that cross-domain objectreferences are correctly handled. For example, if you add a user from one domain to a security group from a different domain, the Infrastructure Master makes sure this is done properly. As you can guess however, if your Active Directory deployment has only a single domain, then the Infrastructure Master role does no work at all, and even in a multi-domain environment it is rarely used except when complex user administration tasks are performed, so the machine holding this role doesn’t need to have much horsepower at all.
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/223346
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Flexible_single_master_operation
QUESTION 139
You have a server named Server 1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has a thin provisioned disk named Disk1. You need to expand Disk1. Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
A. From File and Storage Services, extend Disk1.
B. From File and Storage Services, add a physical disk to the storage pool.
C. From Disk Management, extend the volume.
D. From Disk Management, delete the volume, create a new volume, and then format the volume.
E. From File and Storage Services, detach Disk1.
Answer: AB
Explanation:
Step 1 (B): if required add physical disk capacity.
Step 2 (A): Dynamically extend the virtual disk (not volume). Windows Server 2012 Storage Space subsystem now virtualizes storage by abstracting multiple physical disksinto a logical construct with specified capacity. The process is to group selected physical disks into a container,the so-called storage pool, such that the total capacity collectively presented by those associated physicaldisks can appear and become manageable as a single and seemingly continuous space. Subsequently astorage administrator creates a virtual disk based on a storage pool, configure a storage layout which isessentially a RAID level, and expose the storage of the virtual disk as a drive letter or a mapped folder inWindows Explorer.
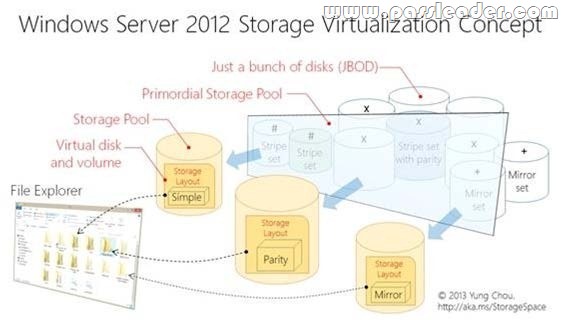
The system administrator uses File and Storage Services in Server Manager or the Disk Management tool torescan the disk, bring the disk online, and extend the disk size.
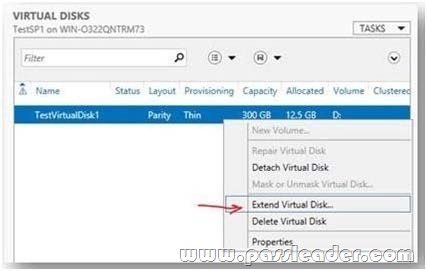
http://blogs.technet.com/b/yungchou/archive/2012/08/31/windows-server-2012-storagevirtualization-explained.aspx
QUESTION 140
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a member server named HVServer1. HVServer1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2 and has the Hyper-V server role installed. HVServer1 hosts two virtual machines named Server1 and Server2. Both virtual machines connect to a virtual switch named Switch1. On Server2, you install a network monitoring application named App1. You need to capture all of the inbound and outbound traffic to Server1 by using App1. Which two commands should you run from Windows PowerShell? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
A. Get-VM “Server2” | Set-VMNetworkAdapter -IovWeight 1
B. Get-VM “Server1” | Set-VMNetworkAdapter -Allow/Teaming On
C. Get-VM “Server1” | Set-VMNetworkAdapter -PortMirroring Source
D. Get-VM “Server2” | Set-VMNetworkAdapter -PortMirroring Destination
E. Get-VM “Server1” | Set-VMNetworkAdapter -IovWeight 0
F. Get-VM “Server2” | Set-VMNetworkAdapter -AllowTeaming On
Answer: CD
Explanation:
C: Catching the traffic from Server1.
D: Catching the traffic to Server1.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh848479%28v=wps.620%29.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh848457%28v=wps.620%29.aspx
QUESTION 141
Drag and Drop Question
You plan to deploy a DHCP server that will support four subnets. The subnets will be configured as shown in the following table.

You need to identify which network ID you should use for each subnet. What should you identify? To answer, drag the appropriate network ID to the each subnet in the answer area.

QUESTION 142
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named adatum.com. The domain contains a file server named Server2 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server2 contains a shared folder named Home. Home contains the home folder of each user. All users have the necessary permissions to access only their home folder. A user named User1 opens the Home share as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
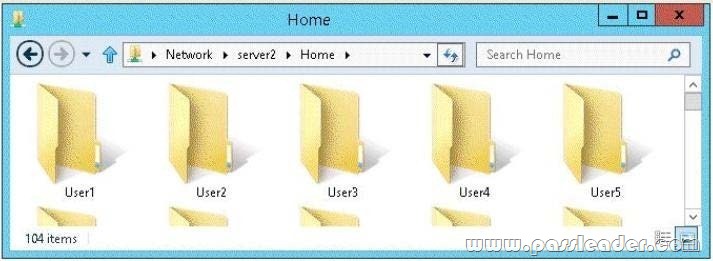
You need to ensure that all users see only their own home folder when they access Home. What should you do from Server2?
A. From Windows Explorer, modify the properties of Home.
B. From Server Manager, modify the properties of the volume that contains Home.
C. From Windows Explorer, modify the properties of the volume that contains Home.
D. From Server Manager, modify the properties of Home.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Access-based Enumeration is a new feature included with Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 1. This feature based file servers to list only the files and folders to which they have allows users of Windows Server 2003 access when browsing content on the file server. This eliminates user confusion that can be caused when users connect to a file server and encounter a large number of files and folders that they cannot access. Access-based Enumeration filters the list of available files and folders on a server to include only those that the requesting user has access to. This change is important because this allows users to see only those files and directories that they have access to and nothing else. This mitigates the scenario where unauthorized users might otherwise be able to see the contents of a directory even though they don’t have access to it. Access-Based Enumeration (ABE) can be enabled at the Share properties through Server Manager.

After implementation instead of seeing all folder including the ones the user does not have access to:

User will have access just to the folder where has rights to:
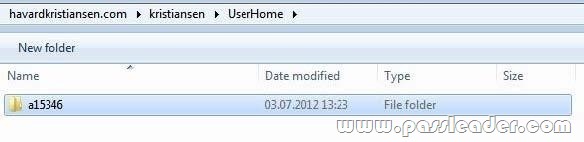
If a user with full access browses the same folder it will show all 5230 folders.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc784710%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/pt-pt/library/dd772681%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 143
You have a server named Server1 that runs a Server Core Installation of Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter. You have a WIM file that contains the four images of Windows Server 2012 R2 as shown in the Images exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)

You review the installed features on Server1 as shown in the Features exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
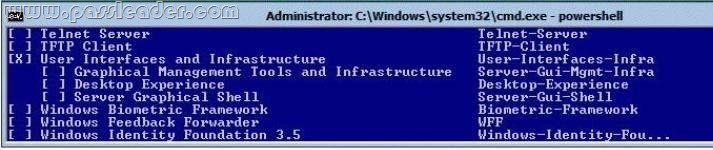
You need to install the Server Graphical Shell feature on Server1. Which two possible sources can you use to achieve this goal? (Each correct answer presents a complete solution. Choose two.)
A. Index 1
B. Index 2
C. Index 3
D. Index 4
Answer: BD
Explanation:
When you install Windows Server 2012 R2 you can choose between Server Core Installation and Server with a GUI. The “Server with a GUI” option is the Windows Server 2012 R2 equivalent of the Full installation option available in Windows Server 2008 R2. The “Server Core Installation” option reduces the space required on disk, the potential attack surface, and especially the servicing requirements, so we recommend that you choose the Server Core installation unless you have a particular need for the additional user interface elements and graphical management tools that are included in the “Server with a GUI” option. For this reason, the Server Core installation is now the default. Because you can freely switch between these options at any time later, one approach might be to initially install the Server with a GUI option, use the graphical tools to configure the server, and then later switch to the Server Core Installation option. Reference: Windows Server Installation Options
QUESTION 144
Your network contains two subnets. The subnets are configured as shown in the following table.

You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 is connected to LAN1. You run the route print command as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)

You need to ensure that Server1 can communicate with the client computers on LAN2. What should you do?
A. Change the default gateway address.
B. Set the state of the Teredo interface to disable.
C. Change the metric of the 10.10.1.0 route.
D. Set the state of the Microsoft ISATAP Adapter #2 interface to disable.
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPv4#Addresses_ending_in_0_or_255
QUESTION 145
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. All servers run Windows Server 2012 R2. The domain contains a member server named Server1. Server1 has the File Server server role installed. On Server1, you create a share named Documents. The Documents share will contain the files and folders of all users. You need to ensure that when the users connect to Documents, they only see the files to which they have access. What should you do?
A. Modify the NTFS permissions.
B. Modify the Share permissions.
C. Enable access-based enumeration.
D. Configure Dynamic Access Control.
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc784710%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/pt-pt/library/dd772681%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 146
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. You have a starter Group Policy Object (GPO) named GPO1 that contains more than 100 settings. You need to create a new starter GPO based on the settings in GPO1. You must achieve this goal by using the minimum amount of administrative effort. What should you do?
A. Run the New-GPStarterGPO cmdlet and the Copy-GPO cmdlet.
B. Create a new starter GPO and manually configure the policy settings of the starter GPO.
C. Right-click GPO1, and then click Back Up.
Create a new starter GPO.
Right-click the new GPO, and then click Restore from Backup.
D. Right-click GPO1, and then click Copy.
Right-click Starter GPOs, and then click Paste.
Answer: A
Explanation:
The New-GPStarterGPO cmdlet creates a Starter GPO with the specified name. If the Starter GPOs folder does not exist in the SYSVOL when the New-GPStarterGPO cmdlet is called, it is created and populated with the eight Starter GPOs that ship with Group Policy. The Copy-GPO cmdlet creates a (destination) GPO and copies the settings from the source GPO to the new GPO. The cmdlet can be used to copy a GPO from one domain to another domain within the same forest. You can specify a migration table to map security principals and paths when copying across domains. You can also specify whether to copy the access control list (ACL) from the source GPO to the destination GPO.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee461063.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee461050.aspx
QUESTION 147
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a member server named Server1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2 and has the DHCP Server server role installed. You create two IPv4 scopes on Server1. The scopes are configured as shown in the following table.

The DHCP clients in Subnet1 can connect to the client computers in Subnet2 by using an IP address or a FQDN. You discover that the DHCP clients in Subnet2 can connect to client computers in Subnet1 by using an IP address only. You need to ensure that the DHCP clients in both subnets can connect to any other DHCP client by using a FQDN. What should you add?
A. The 006 DNS Servers option to Subnet2
B. The 015 DNS Domain Name option to Subnet1
C. The 006 DNS Servers option to Subnet1
D. The 015 DNS Domain Name option to Subnet2
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee941136%28v=WS.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 148
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains two servers named Server1 and Server2. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server2 runs Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 (SP1) and has the DHCP Server server role installed. You need to manage DHCP on Server2 by using the DHCP console on Server1. What should you do first?
A. From Windows PowerShell on Server2, run Enable-PSRemoting cmdlet.
B. From Windows PowerShell on Server1, run Install-WindowsFeature.
C. From Windows Firewall with Advanced Security on Server2, create an inbound rule.
D. From Internet Explorer on Server2, download and install Windows Management Framework 3.0.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Original answer is A. When the DHCP role is installed, it appears that the firewall rules are automatically added. This means you only need to add the DHCP Manager MMC snap-in which is a Role Administration Tool feature. So the correct answer must be B.
QUESTION 149
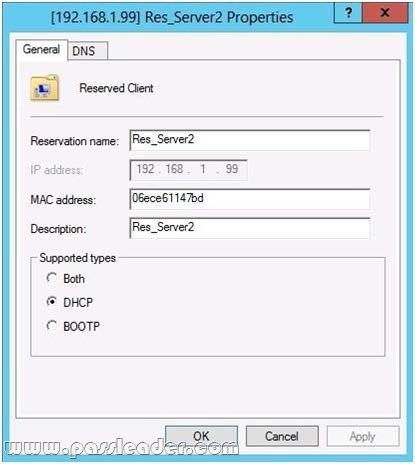
Your network contains two servers named Server1 and Server2 that run Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 is a DHCP server that is configured to have a scope named Scope1. Server2 is configured to obtain an IP address automatically. In Scope1, you create a reservation named Res_Server2 for Server2. A technician replaces the network adapter on Server2. You need to ensure that Server2 can obtain the same IP address. What should you modify on Server1?
A. The Advanced settings of Res_Server2
B. The MAC address of Res Server2
C. The Network Access Protection Settings of Scope1
D. The Name Protection settings of Scope1
Answer: B
Explanation:
For clients that require a constant IP address, you can either manually configure a static IP address, or assigna reservation on the DHCP server. Reservations are permanent lease assignments that are used to ensure that a specified client on a subnet can always use the same IP address. You can use DHCP reservations for hosts that require a consistent IP address, but do not need to be statically configured. DHCP reservations provide a mechanism by which IP addresses may be permanently assigned to aspecific client based on the MAC address of that client. The MAC address of a Windows client can be found running the ipconfig /all command. For Linux systems the corresponding command is ifconfig -a. Once the MAC address has been identified, the reservation may be configured using either the DHCP consoleor at the command prompt using the netsh tool.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc779507%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/170062/en-us
QUESTION 150
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. An organizational unit (OU) named OU1 contains the user accounts and the computer accounts for laptops and desktop computers. A Group Policy Object (GPO) named GP1 is linked to OU1. You need to ensure that the configuration settings in GP1 are applied only to the laptops in OU1. The solution must ensure that GP1 is applied automatically to new laptops that are added to OU1. What should you do?
A. Modify the GPO Status of GP1.
B. Configure the WMI Filter of GP1.
C. Modify the security settings of GP1.
D. Modify the security settings of OU1.
Answer: B
Explanation:
WMI filtering
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) filters allow you to dynamically determine the scope of Group Policy Objects (GPOs) based on attributes of the target computer. When a GPO that is linked to a WMI filter is applied on the target computer, the filter is evaluated on the target computer. If the WMI filter evaluates to false, the GPO is not applied (except if the client computer is running Windows Server, in which case the filteris ignored and the GPO is always applied). If the WMI filter evaluates to true, the GPO is applied.
WMI filtering using GPMC
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) filters allow you to dynamically determine the scope of Group Policy Objects (GPOs) based on attributes of the target computer. When a GPO that is linked to a WMI filter is applied on the target computer, the filter is evaluated on the target computer. If the WMI filter evaluates to false, the GPO is not applied (except if the client computer is running Windows Server, in which case the filter is ignored and the GPO is always applied). If the WMI filter evaluates to true, the GPO is applied. WMI filters, like GPOs, are stored on a per-domain basis. A WMI filter and the GPO it is linked to must be in the same domain.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc779036%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 151
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. All client computer accounts are in an organizational unit (OU) named AllComputers. Client computers run either Windows 7 or Windows 8. You create a Group Policy Object (GPO) named GP1. You link GP1 to the AllComputers OU. You need to ensure that GP1 applies only to computers that have more than 8 GB of memory. What should you configure?
A. The Security settings of AllComputers
B. The Security settings of GP1
C. The WMI filter for GP1
D. The Block Inheritance option for AllComputers
Answer: C
Explanation:
Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) filters allow you to dynamically determine the scope of Group Policy Objects (GPOs) based on attributes of the target computer. When a GPO that is linked to a WMI filter is applied on the target computer, the filter is evaluated on the target computer. If the WMI filter evaluates to false, the GPO is not applied (except if the client computer is running Windows Server, in which case the filter is ignored and the GPO is always applied). If the WMI filter evaluates to true, the GPO is applied. WMI filters, like GPOs, are stored on a per-domain basis. A WMI filter and the GPO it is linked to must be in the same domain.


QUESTION 152
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains two servers named Server1 and Server2. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server2 runs Windows Server 2008 R2 Service Pack 1 (SP1) and has the DHCP Server server role installed. You need to manage DHCP on Server2 by using the DHCP console on Server1. What should you do first?
A. From Windows Firewall with Advanced Security on Server2, create an inbound rule.
B. From Internet Explorer on Server2, download and install Windows Management Framework 3.0.
C. From Server Manager on Server1, install a feature.
D. From Windows PowerShell on Server2, run Enable PSRemoting.
Answer: C
Explanation:
When the DHCP role is installed, it appears that the firewall rules are automatically added. This means you only need to add the DHCP Manager MMC snap-in which is a Role Administration Tool feature.
QUESTION 153
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a member server named HVServer1. HVServer1 runs Windows Server 2012 and has the Hyper-V server role installed. HVServer1 hosts 10 virtual machines. All of the virtual machines connect to a virtual switch named Switch1. Switch1 is configured as a private network. All of the virtual machines have the DHCP guard and the router guard settings enabled. You install the DHCP server role on a virtual machine named Server 1. You authorize Server1 as a DHCP server in contoso.com. You create an IP scope. You discover that the virtual machines connected to Switch1 do not receive IP settings from Server1. You need to ensure that the virtual machines can use Server1 as a DHCP server. What should you do?
A. Enable MAC address spoofing on Server1.
B. Disable the DHCP guard on all of the virtual machines that are DHCP clients.
C. Disable the DHCP guard on Server1.
D. Enable single-root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV) on Server1.
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj679878.aspx#bkmk_dhcp
http://blogs.technet.com/b/jhoward/archive/2008/06/17/hyper-v-what-are-the-uses-for-different-types-of-virtual-networks.aspx
QUESTION 154
Hotspot Question
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named adatum.com. You create an account for a temporary employee named User1. You need to ensure that User1 can log on to the domain only between 08:00 and 18:00 from a client computer named Computer1. From which tab should you perform the configuration? To answer, select the appropriate tab in the answer area.
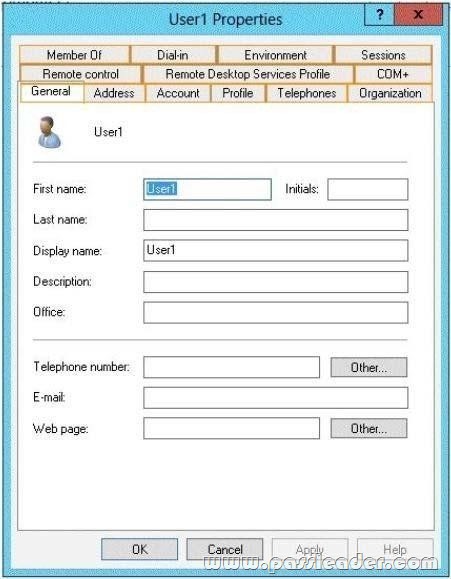
Answer:
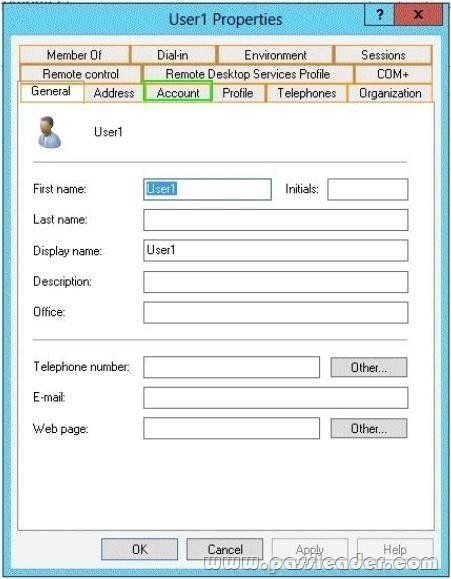
Explanation:
To set logon hours:
1. Open Active Directory Users and Computers.
2. In the console tree, click Users.
3. Right-click the user account, and then click Properties.
4. On the Account tab, click Logon Hours, and then set the permitted or denied logon hours for the user.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc740199(v=ws.10).aspx
QUESTION 155
You work as a senior administrator at contoso.com. The contoso.com network consists of a single domain named contoso.com. All servers on the contoso.com network have Windows Server 2012 R2 installed. You are running a training exercise for junior administrators. You are currently discussing the new VHD format called VHDX. Which of the following is TRUE with regards to VHDX? (Choose all that apply.)
A. It supports virtual hard disk storage capacity of up to 64GB.
B. It supports virtual hard disk storage capacity of up to 64TB.
C. It does not provide protection against data corruption during power failures.
D. It has the ability to store custom metadata about the file that the user might want to record.
Answer: BD
Explanation:
The main new features of the VHDX format are:
– Support for virtual hard disk storage capacity of up to 64TB.
– Protection against data corruption during power failures by logging updates to the VHDX metadata structures. Improved alignment of the virtual hard disk format to work well on large sector disks.
The VHDX format also provides the following features:
– Larger block sizes for dynamic and differencing disks, which allows these disks to attune to the needs of the workload.
– A 4KB logical sector virtual disk that allows for increased performance when used by applications and workloads that are designed for 4KB sectors.
– The ability to store custom metadata about the file that the user might want to record, such as operating system version or patches applied.
– Efficiency in representing data (also known as “trim”), which results in smaller file size and allows the underlying physical storage device to reclaim unused space. (Trim requires physical disks directly attached to a virtual machine or SCSI disks, and trim-compatible hardware.)
VHDX Format – Features and Benefits
VHDX format features provide features at the virtual hard disk as well as virtual hard disk file layers and is optimized to work well with modern storage hardware configurations and capabilities. At the virtual hard disk layer, benefits include the ability to represent a large virtual disk size up to 64TB, support larger logical sector sizes for a virtual disk up to 4 KB that facilitates the conversion of 4KB sector physical disks to virtual disks, and support large block sizes for a virtual disk up to 256MB that enables tuning block size to match the IO patterns of the application or system for optimal performance. At the virtual hard disk file layer, the benefits include the use of a log to ensure resiliency of the VHDX file to corruptions from system power failure events and a mechanism that allows for small pieces of user generated data to be transported along with the VHDX file. On modern storage platforms, the benefits include optimal performance on host disks that have physical sector sizes larger than 512 bytes through improved data alignment and capability to use the information from the UNMAP command, sent by the application or system using the virtual hard disk, to optimize the size of the VHDX file. The format is designed so that additional features could be introduced in the future by Microsoft or extended by other parser implementations. The format provides parsers the ability to detect features in a VHDX file that a parser does not understand.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831446.aspx
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=34750
QUESTION 156
You have a server named Server1 that runs a Server Core Installation of Windows Server 2012 R2. You attach a 4-TB disk to Server1. The disk is configured as an MBR disk. You need to ensure that you can create a 4-TB volume on the disk. Which Diskpart command should you use?
A. Automount
B. Convert
C. Expand
D. Attach
Answer: B
Explanation:
You can use Diskpart to convert a basic disk to a dynamic disk. The basic disk can either be empty or contain either primary partitions or logical drives. The basic disk can be a data disk or system or boot drive. A MBR file structure is only capable of 2TB maximum. The disk will have to be converted to a GPT file structure. GPT is capable of 18 exabytes volumes. Convert gpt – Converts an empty basic disk with the master boot record (MBR) partition style into a basic disk with the GUID partition table (GPT) partition style. The disk may be a basic or a dynamic disk but it must not contain any valid data partitions or volumes.
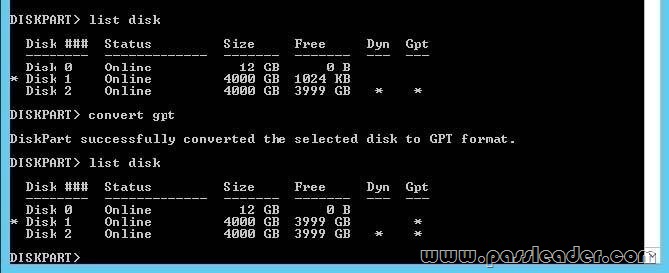
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc766465(v=ws.10).aspx
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/300415/en-us
QUESTION 157
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a server named Server1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2. You need to create 3-TB virtual hard disk (VHD) on Server1. Which tool should you use?
A. Server Manager
B. Diskpart
C. New-StoragePool
D. New-VirtualDisk
Answer: B
Explanation:
New-VirtualDisk – Creates a new virtual disk in the specified storage pool. Although the new Server Manager UI in Windows Server 2012 R2 provides a very convenient and intuitive workflow to provision and manage Storage, interaction with PowerShell is required to access many of the advanced features. If I then create a simple 200GB Virtual Disk via the UI named VDiskSimpleUI, the resulting Virtual Disk leverages 8 columns and maintains 1 copy of the data. But when creating the Virtual Disk via PowerShell, I can force the tripping across all nine of the disks and optimize performance.
……
http://blogs.technet.com/b/wincat/archive/2012/05/21/optimizing-windows-server-2012-storagemanagement-via-powershell-for-both-performance-and-resiliency.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh848643%28v=wps.620%29.aspx
QUESTION 158
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. All domain controllers run Windows Server 2012 R2. You create and enforce the default AppLocker executable rules. Users report that they can no longer execute a legacy application installed in the root of drive C. You need to ensure that the users can execute the legacy application. What should you do?
A. Modify the action of the existing rules.
B. Create a new rule.
C. Add an exception to the existing rules.
D. Delete an existing rule.
Answer: B
Explanation:
AppLocker is a feature that advances the functionality of the Software Restriction Policies feature. AppLocker contains new capabilities and extensions that reduce administrative overhead and help administrators control how users can access and use files, such as executable files, scripts, Windows Installer files, and DLLs. By using AppLocker, you can:
– Define rules based on file attributes that persist across application updates, such as the publisher name (derived from the digital signature), product name, file name, and file version. You can also create rules based on the file path and hash.
– Assign a rule to a security group or an individual user.
– Create exceptions to rules. For example, you can create a rule that allows all users to run all Windows binaries except the Registry Editor (Regedit.exe).
– Use audit-only mode to deploy the policy and understand its impact before enforcing it..
– Create rules on a staging server, test them, export them to your production environment, and then import them into a Group Policy Object.
……
http://technet.microsoft.com/library/hh831440.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd759068.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/de-de/library/hh994621.aspx
QUESTION 159
You have two servers named Server! and Server2. Both servers run Windows Server 2012 R2. The servers are configured as shown in the following table.

The routing table for Server1 is shown in the Routing Table exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
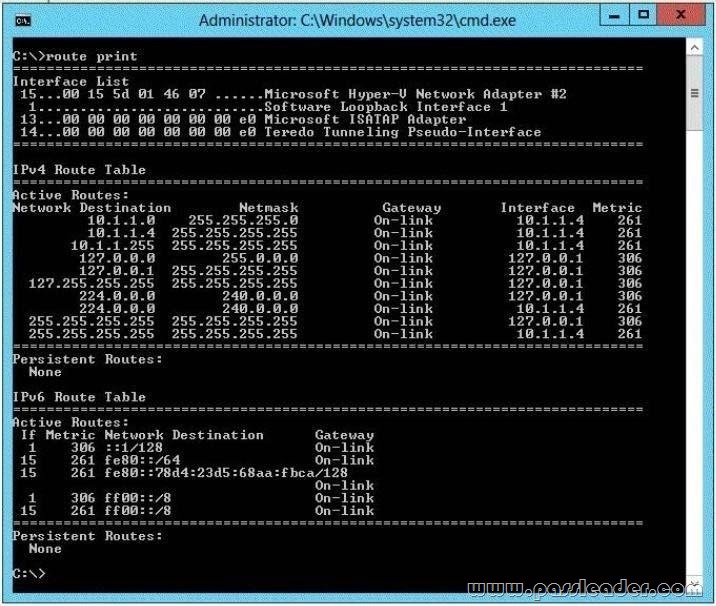
From Server1, you attempt to ping Server2, but you receive an error message as shown in the Error exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)

You need to ensure that you can successfully ping Server2 from Server1. What should you do on Server1?
A. Disable Windows Firewall.
B. Modify the default gateway settings.
C. Modify the DNS settings.
D. Modify the subnet mask.
Answer: B
Explanation:
Route is used to view and modify the IP routing table. Route Print displays a list of current routes that the host knows. Default gateways are important to make IP routing work efficiently. TCP/IP hosts rely on default gateways for most of their communication needs with hosts on remote network segments. In this way, individual hosts are freed of the burden of having to maintain extensive and continuously updated knowledge about individual remote IP network segments. Only the router that acts as the default gateway needs to maintain this level of routing knowledge to reach other remote network segments in the larger internetwork. In order for Host A on Network 1 to communicate with Host B on Network 2, Host A first checks its routing table to see if a specific route to Host B exists. If there is no specific route to Host B, Host A forwards its TCP/IP traffic for Host B to its own default gateway, IP Router 1.

http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc779696%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc958877.aspx
QUESTION 160
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has the Hyper-V server role installed. The domain contains a virtual machine named VM1. A developer wants to attach a debugger to VM1. You need to ensure that the developer can connect to VM1 by using a named pipe. Which virtual machine setting should you configure?
A. Network Adapter
B. BIOS
C. Processor
D. COM 1
Answer: D
Explanation:
Named pipe. This option connects the virtual serial port to a Windows named pipe on the host operating system or a computer on the network. A named pipe is a portion of memory that can be used by one process to pass information to another process, so that the output of one is the input of the other. The second process can be local (on the same computer as the first) or remote (on a networked computer). For example, a local named pipe path could be \\.\pipe\mypipename. Named pipes can be used to create a virtual null modem cable between two virtual machines, or between avirtual machine and a debugging program on the host operating system that supports the use of named pipes. By connecting two virtual serial ports to the same named pipe, you can create a virtual null modem cable connection. Named pipes are useful for debugging or for any program that requires a null modem connection.

http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee449417(v=ws.10).aspx
http://blogs.msdn.com/b/ntdebugging/archive/2011/12/30/configuring-a-hyper-v-vm-forkernel-debugging.aspx
Get the newest PassLeader 70-410 VCE dumps here: http://www.passleader.com/70-410.html (512 Q&As Dumps –> 528 Q&As Dumps)
And, DOWNLOAD the newest PassLeader 70-410 PDF dumps from Cloud Storage for free: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpfnJzOE1fWnlJOWVtaE93SnJNT3gtaTNYYnVpZkw5THBSMWRKbFlfaXh1azg

