Valid 70-410 Dumps shared by PassLeader for Helping Passing 70-410 Exam! PassLeader now offer the newest 70-410 VCE dumps and 70-410 PDF dumps, the PassLeader 70-410 exam questions have been updated and ANSWERS have been corrected, get the newest PassLeader 70-410 dumps with VCE and PDF here: http://www.passleader.com/70-410.html (512 Q&As Dumps –> 528 Q&As Dumps)
BTW, DOWNLOAD part of PassLeader 70-410 dumps from Cloud Storage: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpfnJzOE1fWnlJOWVtaE93SnJNT3gtaTNYYnVpZkw5THBSMWRKbFlfaXh1azg
QUESTION 161
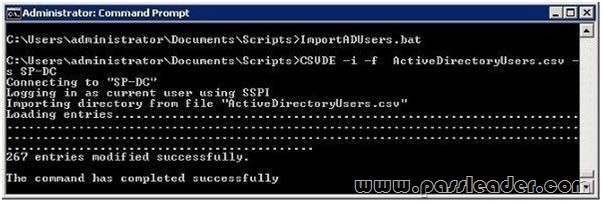
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. Your company hires 500 temporary employees for the summer. The human resources department gives you a Microsoft Excel document that contains a list of the temporary employees. You need to automate the creation of user accounts for the 500 temporary employees. Which tool should you use?
A. The Add-Member cmdlet
B. ADSI Edit
C. The csvde.exe command
D. Active Directory Users and Computers
Answer: C
Explanation:
Csvde.exe is the best option to add multiple users. As you just need to export the excel spreadsheet as a csv file and make sure the parameters are correct. You can use Csvde to import and export Active Directory data that uses the comma-separated value format. Use a spreadsheet program such as Microsoft Excel to open this .csv file and view the header and value information.
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/327620/en-us
QUESTION 162
Your network contains two subnets. The subnets are configured as shown in the following table.

You have a server named Server2 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server2 is connected to LAN1. You run the route print command as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)

You need to ensure that Server2 can communicate with the client computers on LAN2. What should you do?
A. Change the metric of the 10.10.1.0 route.
B. Set the state of the Teredo interface to disable.
C. Set the state of the Microsoft ISATAP Adapter #2 interface to disable.
D. Run route delete 172.23.2.0.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Route is used to view and modify the IP routing table. Route Print displays a list of current routes that the host knows. Default gateways are important to make IP routing work efficiently. TCP/IP hosts rely on default gateways for most of their communication needs with hosts on remote network segments. In this way, individual hosts are freed of the burden of having to maintain extensive and continuously updated knowledge about individual remote IP network segments. Only the router that acts as the default gateway needs to maintain this level of routing knowledge to reach other remote network segments in the larger internetwork. If the default gateway fails, communication beyond the local network segment may be impaired. To prevent this, you can use the Advanced TCP/IP Settings dialog box (in Network Connections) for each connection to specify multiple default gateways. You can also use the route command to manually add routes to the routing table for heavily used hosts or networks. If you have multiple interfaces and you configure a default gateway for each interface, TCP/IP by default automatically calculates an interface metric that is based on the speed of the interface. The interface metric becomes the metric of the default route in the routing table for the configured default gateway. The interface with the highest speed has the lowest metric for its default route. The result is that whenever multiple default gateways are configured on multiple interfaces, the fastest interface will be used to forward traffic to its default gateway. If multiple interfaces of the same speed have the same lowest interface metric, then, based upon the binding order, the default gateway of the first network adapter is used. The default gateway for the second network adapter is used when the first is unavailable. In order for Host A on Network 1 to communicate with Host B on Network 2, Host A first checks its routing table to see if a specific route to Host B exists. If there is no specific route to Host B, Host A forwards its TCP/IP traffic for Host B to its own default gateway, IP Router 1.

http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc779696%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc958877.aspx
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/299540/en-us
QUESTION 163
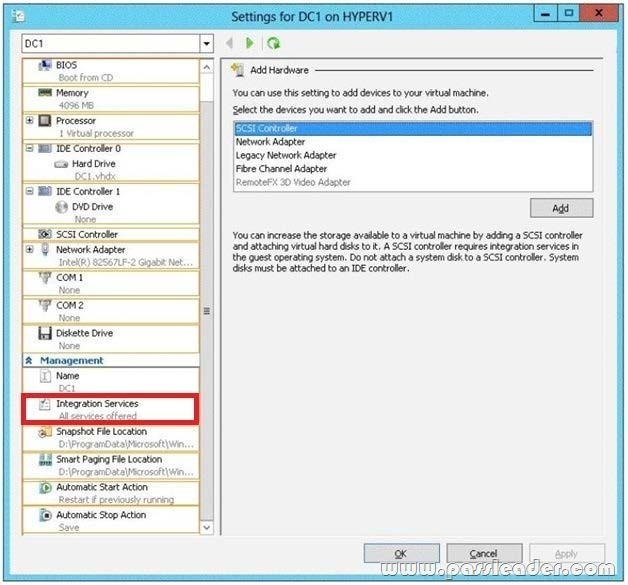
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a server named Server1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2 and has the Hyper-V server role installed. You need to log the amount of system resources used by each virtual machine. What should you do?
A. From Windows PowerShell, run the Enable-VMRe5ourceMetering cmdlet.
B. From Windows System Resource Manager, enable Accounting.
C. From Windows System Resource Manager, add a resource allocation policy.
D. From Windows PowerShell, run the Measure-VM cmdlet.
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc779696%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc958877.aspx
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/299540/en-us
QUESTION 164
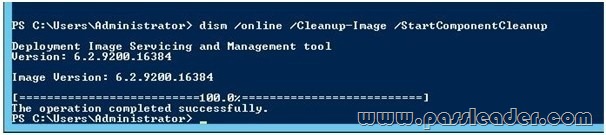
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. You plan to create an image of Server1. You need to remove the source files for all server roles that are not installed on Server1. Which tool should you use?
A. servermanagercmd.exe
B. imagex.exe
C. dism.exe
D. ocsetup.exe
Answer: C
Explanation:
servermanagercmd.exe – The servermanagercmd.exe command-line tool has been deprecated in Windows Server 2008 R2.
imagex.exe – ImageX is a command-line tool in Windows Vista that you can use to create and manage Windows image (.wim) files. A .wim file contains one or more volume images, disk volumes that contain images of an installed Windows operating system.
dism.exe – Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM.exe) is a command-line tool that can be used to service a Windows image or to prepare a Windows Preinstallation Environment (WindowsPE) image. It replaces Package Manager (pkgmgr.exe), PEimg, and Intlcfg that were included in Windows Vista. The functionality that was included in these tools is now consolidated in one tool (DISM.exe), and new functionality has been added to improve the experience for offline servicing. DISM can Add, remove, and enumerate packages.
ocsetup.exe – The ocsetup.exe tool is used as a wrapper for Package Manager (pkgmgr.exe) and for WindowsInstaller (Msiexec.exe). ocsetup.exe is a command-line utility that can be used to perform scripted installs and scripted uninstalls of Windows optional components. The ocsetup.exe tool replaces the sysocmgr.exe tool that Windows XP and Windows Server 2003 use.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh824822.aspx
http://blogs.technet.com/b/joscon/archive/2010/08/26/adding-features-with-dism.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831809.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh825265.aspx
QUESTION 165
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. An administrator provides you with a file that contains the information to create user accounts for 200 temporary employees. The file is shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)

You need to automate the creation of the user accounts. You must achieve this goal by using the minimum amount of administrative effort. Which tool should you use?
A. csvde
B. Net user
C. Ldifde
D. Dsadd
Answer: A
Explanation:
csvde – Imports and exports data from Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) using files that store data in the comma-separated value (CSV) format. You can also support batch operations based on the CSV file format standard.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc732101(v=ws.10).aspx
Net user – Adds or modifies user accounts, or displays user account information.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc771865(v=ws.10).aspx
Ldifde – Creates, modifies, and deletes directory objects. You can also use ldifde to extend the schema, export Active Directory user and group information to other applications or services, and populate Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) with data from other directory services.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731033(v=ws.10).aspx
Dsadd – Adds specific types of objects to the directory.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc753708(v=ws.10).aspx
csvde.exe is the best option to add multiple users. as you just need to export the excel spreadsheet as a csv file and make sure the parameters are correct. You can use Csvde to import and export Active Directory data that uses the comma-separated value format. Use a spreadsheet program such as Microsoft Excel to open this .csv file and view the header and value information

http://support.microsoft.com/kb/327620/en-us
QUESTION 166
Hotspot Question
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. All client computers run Windows 8. An administrator creates an application control policy and links the policy to an organizational unit (OU) named OU1. The application control policy contains several deny rules. The deny rules apply to the Everyone group. You need to prevent users from running the denied application. What should you configure? To answer, select the appropriate object in the answer area.
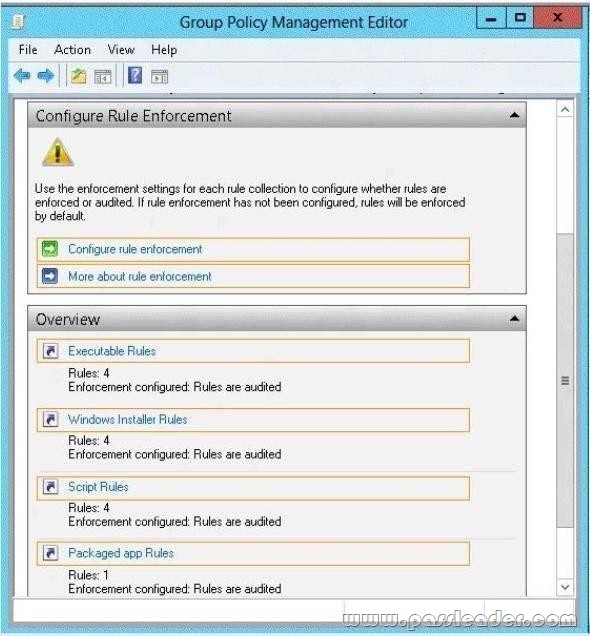
Answer:

Explanation:
To enable the enforce rules enforcement setting by using the Local Security Policy snap-in:
1. Click Start, type secpol.msc in the search programs and files box, and then press ENTER.
2. If the User Account Control dialog box appears, confirm that the action it displays is what you want, and then click Yes.
3. In the console tree, double-click Application Control Policies, right-click AppLocker, and then click Properties.
4. On the Enforcement tab, select the Configured check box for the rule collection that you want to enforce, and then verify that Enforce rules is selected in the list for that rule collection.
5. Repeat step 4 to configure the enforcement setting to Enforce rules for additional rule collections.
6. Click OK.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee791885(v=ws.10).aspx
QUESTION 167
You have a print server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. You discover that when there are many pending print jobs, the system drive occasionally runs out of free space. You add a new hard disk to Server1. You create a new NTFS volume. You need to prevent the print jobs from consuming disk space on the system volume. What should you modify?
A. the properties of the Print Spooler service
B. the Print Server Properties
C. the properties of each shared printer
D. the properties on the new volume
Answer: B
Explanation:
Windows spools print jobs by default to the following directory as the they are processed:
%SystemRoot%\SYSTEM32\SPOOL\PRINTERS.
It is possible for the administrator of a Windows print server to manually instruct Windows the location forplacing the spool files, if for example there is a concern for disk space.

http://support.microsoft.com/kb/137503/en-us
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc757764%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc736979%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 168
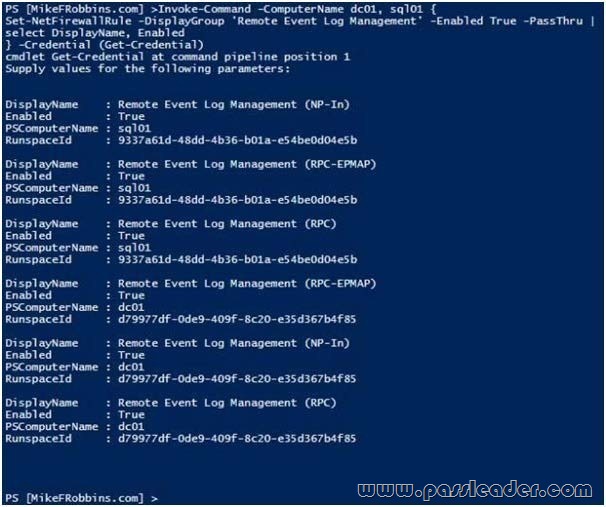
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains an application server named Server1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2. You have a client application named App1 that communicates to Server1 by using dynamic TCP ports. On Server1, a technician runs the following command:
New-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName AllowDynamic -Direction Outbound -LocalPort 1024- 65535 -Protocol TCP
Users report that they can no longer connect to Server1 by using App1.You need to ensure that App1 can connect to Server1. What should you run on Server1?
A. Set-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName AllowDynamic -Action Allow
B. netsh advfirewall firewall set rule name=allowdynamic new action=allow
C. Set-NetFirewallRule -DisplayName AllowDynamic -Direction Inbound
D. netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name=allowdynamic action=allow
Answer: C
Explanation:
Set-NetFirewallRule – Modifies existing firewall rules. You have to allow the connection INTO the server – inbound rules.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj573828%28v=wps.620%29.aspx
http://mikefrobbins.com/2013/02/28/use-powershell-to-remotely-enable-firewall-exceptionson-windows-server-2012/
QUESTION 169
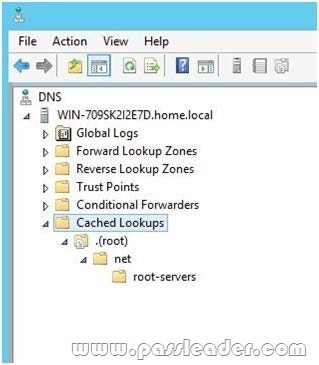
You have a server named dc2.contoso.com that runs Windows Server 2012 R2 and has the DNS Server server role installed. You open DNS Manager as shown in the exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)
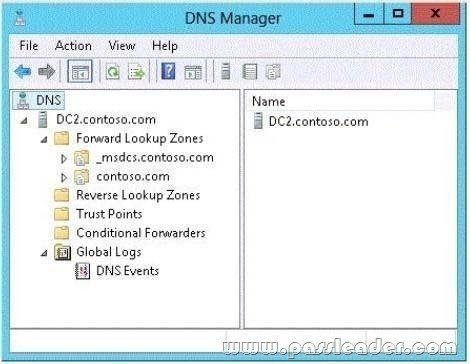
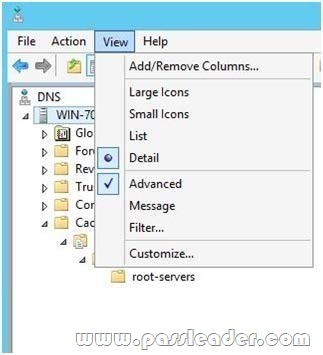
You need to view the DNS server cache from DNS Manager. What should you do first?
A. From the View menu, click Advanced.
B. From the Action menu, click Configure a DNS Server.
C. From the View menu, click Filter.
D. From the Action menu, click Properties.
Answer: A
Explanation:
To view the contents of the DNS cache, perform the following steps:
1. Start the Microsoft Management Console (MMC) DNS snap-in (Go to Start, Programs, Administrative Tools, and click DNS).
2. From the View menu, select Advanced.
3. Select the Cached Lookups tree node from the left-hand pane to display the top-level domains (e.g., com, net) under .(root). Expand any of these domains to view the cached DNS information (the actual records will appear in the right-hand pane).
QUESTION 170
You work as an administrator at contoso.com. The contoso.com network consists of a single domain named contoso.com. All servers on the contoso.com network have Windows Server 2012 R2 installed. contoso.com has a server, named PL-SR07, which has two physical disks installed. The C: drive hosts the boot partition, while the D: drive is not being used. Both disks are online. You have received instructions to create a virtual machine on PL-SR07. Subsequent to creating the virtual machine, you have to connect the D: drive to the virtual machine. Which of the following is TRUE with regards to connecting a physical disk to a virtual machine?
A. The physical disk should not be online.
B. The physical disk should be uninstalled and re-installed.
C. The physical disk should be configured as a striped disk.
D. The physical disk should be configured as a mirrored disk.
Answer: A
Explanation:
Your virtual machines can also be connected to physical hard disks on the virtualization server virtual hard disks. (This is sometimes referred to as having a “pass-through” disk connected to a virtual machine.) The physical hard disk that you connect to a virtual machine can also be a network-attached disk, like a logical unit number (LUN) in a storage area network (SAN). A common example is an iSCSI LUN that has been mapped to the virtualization server by using Microsoft iSCSI Initiator. Because the virtualization server sees network-attached storage as local disks, the iSCSI LUN can be connected to a virtual machine. The most important limitation about having a physical hard disk connected to a virtual machine is that it cannot be connected to the virtualization server or to other virtual machines at the same time. The virtual machine must have exclusive access to the physical hard disk.
Pass-through Disk Configuration
Hyper-V allows virtual machines to access storage mapped directly to the Hyper-V server without requiring the volume be configured. The storage can either be a physical disk internal to the Hyper-V server or it can be a Storage Area Network (SAN) Logical Unit (LUN) mapped to the Hyper-V server. To ensure the Guest has exclusive access to the storage, it must be placed in an Offline state from the Hyper-Vserver perspective.
http://blogs.technet.com/b/askcore/archive/2008/10/24/configuring-pass-through-disks-in-hyper-v.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/pt-pt/library/ff404147%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 171
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. You create a new inbound rule by using Windows Firewall with Advanced Security. You need to configure the rule to allow Server1 to accept unsolicited inbound packets that are received through a network address translation (NAT) device on the network. Which setting in the rule should you configure?
A. Edge traversal
B. Authorized computers
C. Interface types
D. Remote IP address
Answer: A
Explanation:
Edge traversal – This indicates whether edge traversal is enabled (Yes) or disabled (No). When edge traversal is enabled, the application, service, or port to which the rule applies is globally addressable and accessible from outside a network address translation (NAT) or edge device.

Select one of the following options from the list:
Block edge traversal (default) – Prevent applications from receiving unsolicited traffic from the Internet through a NAT edge device.
Allow edge traversal – Allow applications to receive unsolicited traffic directly from the Internet through a NAT edge device.
Defer to user – Let the user decide whether to allow unsolicited traffic from the Internet through a NAT edge device when an application requests it.
Defer to application – Let each application determine whether to allow unsolicited traffic from the Internet through a NAT edge device.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731927.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd421713%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 172
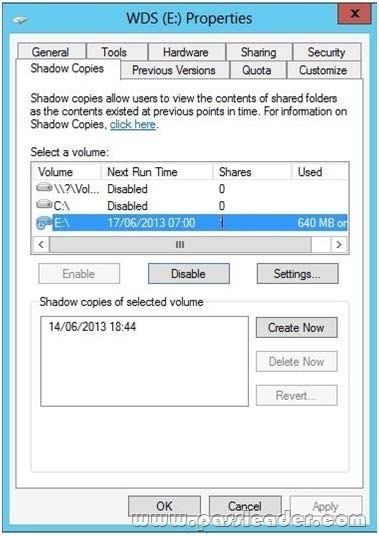
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a member server named Server1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2 and has the File Server server role installed. On Server1, you create a share named Documents. You need to ensure that users can recover files that they accidently delete from Documents. What should you do?
A. Enable shadow copies by using Computer Management.
B. Modify the Startup type of the Volume Shadow Copy Service (VSS) by using the Services console.
C. Create a recovery partition by using Windows Assessment and Deployment Kit (Windows ADK).
D. Create a storage pool that contains a two-way mirrored volume by using Server Manager.
Answer: A
Explanation:
If you enable Shadow Copies of Shared Folders on a volume using the default values, a task will be scheduled to create shadow copies at 7:00 A.M of next business day. The default storage area will be on the same volume, and its size will be 10 percent of the available space. You can only enable Shadow Copies of Shared Folders on a per-volume basis — that is, you cannot select specific shared folders and files on a volume to be copied or not copied. To enable and configure Shadow Copies of Shared Folders:
1. Click Start, point to Administrative Tools, and then click Computer Management.
2. In the console tree, right-click Shared Folders, click All Tasks, and then click Configure Shadow Copies.
3. In Select a volume, click the volume that you want to enable Shadow Copies of Shared Folders for, and then click Enable.
4. You will see an alert that Windows will create a shadow copy now with the current settings and that the settings might not be appropriate for servers with high I/O loads. Click Yes if you want to continue or No if youwant to select a different volume or settings.
5. To make changes to the default schedule and storage area, click Settings.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc771893.aspx
QUESTION 173
You have a server named Server1 that runs a Server Core installation of Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 is configured to obtain an IPv4 address by using DHCP. You need to configure the IPv4 settings of the network connection on Server1 as follows:
– IP address: 10.1.1.1
– Subnet mask: 255.255.240.0
– Default gateway: 10.1.1.254
What should you run?
A. netsh.exe
B. netcfg.exe
C. msconfig.exe
D. ipconfig.exe
Answer: A
Explanation:
In order to configure TCP/IP settings such as the IP address, Subnet Mask, Default Gateway, DNS and WINS addresses and many other options you can use netsh.exe.
Incorrect:
Not D: Windows Server 2012 Core still has IPCONFIG.EXE that can be used to view the IP configuration. Modern servers typically come with several network interface ports. This causes IPCONFIG.EXE to scroll off the screen when viewing its output. Consider piping the output if IPCONFIG.EXE to a file and view it with notepad.exe.
QUESTION 174
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains three member servers. The servers are configured as shown in the following table.
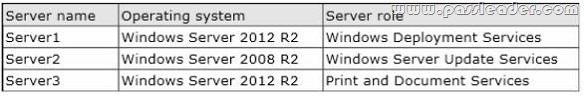
All client computers run Windows 8. All client computers receive updates from Server2. On Servers, you add a shared printer named Printer1. Printer1 uses a Type 4 driver that is not included in the Windows 8 installation media. You need to ensure that when users connect to the printer for the first time, the printer driver is installed automatically on their client computer. What should you do?
A. From the Windows Deployment Services console on Server1, add the driver package for Printer1.
B. From the Update Services console on Server2, import and approve updates.
C. From Windows PowerShell on Server3, run the Add-PrinterDriver cmdlet.
D. From the Print Management console on Server3, add additional drivers for Printer1.
Answer: D
Explanation:
Print and Document Services enables you to centralize print server and network printer tasks. With this role, you can also receive scanned documents from network scanners and route the documents to a shared network resource, Windows SharePoint Services site, or email addresses. Starting with Windows 8 and Server 2012 R2 – here comes the Version 4 drivers (class driver or model specific driver) which changes a couple of things, a system that allows people to install their printers without having to locate a driver for that device in many cases.
1. There is no v3 driver support for Windows on ARM
2. The print server is no longer a software distribution mechanism
3. Group Policy Preference TCP/IP printers do not support Type 4 print drivers
4. The LPR/LPD protocol is deprecated and will eventually be removed
To install v4 drivers using the Print Management Console:
1. Open the Print Management Console by opening Server Manager, click Tools, and then click Print Management.
2. Expand Print Servers, and then expand the Print Server name. Right click Drivers and select Add Drivers.
3. To add a v4 driver for a device, select the driver that has v4 or Class Driver in the name.
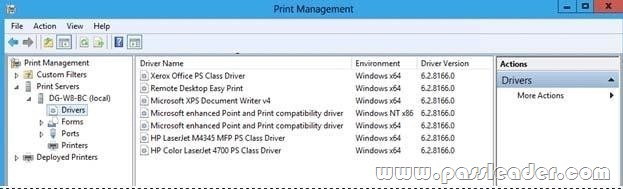
Once installed, v4 drivers are identified by the Version field displayed in the Driver Properties:

The driver name will state Class Driver, the Config File should show PrintConfig.dll, and the driver path should be %systemroot%\system32\DriverStore.
Class Drivers – V4 drivers that ship with Windows Server 2012 R2 are known as Class Drivers. Drivers of this type should always display Class Driver in the name.
Model Specific Drivers – V4 drivers that are downloaded directly from a printer manufacturer website or downloaded from Windows Update are known as model specific drivers.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831468.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj134163.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831769.aspx
http://blogs.technet.com/b/askperf/archive/2012/11/03/windows-8-windows-server-2012-what-s-new-with-printing-in-windows-8.aspx
QUESTION 175
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains 20 computer accounts in an organizational unit (OU) named OU1. A user account named User1 is in an OU named OU2. You are configuring a Group Policy Object (GPO) named GPO1. You need to assign User1 the Back up files and directories user right to all of the computer accounts in OU1. Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
A. Link GPO1 to OU1.
B. Link GPO1 to OU2.
C. Modify the Delegation settings of GPO1.
D. From User Configuration in GPO1, modify the security settings.
E. From Computer Configuration in GPO1, modify the security settings.
Answer: AE
Explanation:
A. You have to Link a GPO to an object in order for it to be Applied to that object.
B. Wrong object to link the GPO.
C. Delegation settings refer to delegating control over the properties of the GPO.
D. User Configuration typically contains subitems for Software Settings, Windows Settings, and AdministrativeTemplates.
E. Backup Files and Directories are found in Computer Configuration\Windows Settings\Local Policies\User Rights Assignment Back up files and directories – this user right determines which users can bypass file and directory, registry,and other persistent object permissions for the purposes of backing up the system.

Specifically, this user right is similar to granting the following permissions to the user or group in question on all files and folders on the system:
– Traverse Folder/Execute File
– List Folder/Read Data
– Read Attributes
– Read Extended Attributes
– Read Permissions
Caution: Assigning this user right can be a security risk. Since there is no way to be sure that a user is backing up data, stealing data, or copying data to be distributed, only assign this user right to trusted users.
Default on workstations and servers: Administrators, Backup Operators.
Default on domain controllers: Administrators, Backup Operators, Server Operators.
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=25250
QUESTION 176
You have an existing Active Directory site named Site1. You create a new Active Directory site and name it Site2. You need to configure Active Directory replication between Site1 and Site2. You install a new domain controller. You create the site link between Site1 and Site2. What should you do next?
A. Use the Active Directory Sites and Services console to configure a new site link bridge object.
B. Use the Active Directory Sites and Services console to decrease the site link cost between Site1 and Site2.
C. Use the Active Directory Sites and Services console to assign a new IP subnet to Site2. Move the new domain controller object to Site2.
D. Use the Active Directory Sites and Services console to configure the new domain controller as a preferred bridgehead server for Site1.
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://www.enterprisenetworkingplanet.com/netsysm/article.php/624411/Intersite-Replication.htm
Inter-site Replication
The process of creating a custom site link has fivebasic steps:
1. Create the site link.
2. Configure the site link’s associated attributes.
3. Create site link bridges.
4. Configure connection objects. (This step is optional.)
5. Designate a preferred bridgehead server. (This step is optional.)
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc759160%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 177
Your company has an Active Directory forest. Not all domain controllers in the forest are configured as Global Catalog Servers. Your domain structure contains one root domain and one child domain. You modify the folder permissions on a file server that is in the child domain. You discover that some Access Control entries start with S-1-5-21 and that no account name is listed. You need to list the account names. What should you do?
A. Move the RID master role in the child domain to a domain controller that holds the Global Catalog.
B. Modify the schema to enable replication of the friendlynames attribute to the Global Catalog.
C. Move the RID master role in the child domain to a domain controller that does not hold the Global Catalog.
D. Move the infrastructure master role in the child domain to a domain controller that does not hold the Global Catalog.
Answer: D
Explanation:
If the IM Flexible Single Master Operation (FSMO) role holder is also a global catalog server, the phantom indexes are never created or updated on that domain controller. (The FSMO is also known as the operations master.) This behavior occurs because a global catalog server contains a partial replica of every object in Active Directory. The IM does not store phantom versions of the foreign objects because it already has a partial replica of the object in the local global catalog. For this process to work correctly in a multidomain environment, the infrastructure FSMO role holder cannot be a global catalog server. Be aware that the first domain in the forest holds all five FSMO roles and is also a global catalog. Therefore, you must transfer either role to another computer as soon as another domain controller is installed in the domain if you plan to have multiple domains.
QUESTION 178
Your company has an Active Directory domain. You log on to the domain controller. The Active Directory Schema snap-in is not available in the Microsoft Management Console (MMC). You need to access the Active Directory Schema snap-in. What should you do?
A. Register Schmmgmt.dll.
B. Log off and log on again by using an account that is a member of the Schema Admins group.
C. Use the Ntdsutil.exe command to connect to the schema master operations master and open the schema for writing.
D. Add the Active Directory Lightweight Directory Services (AD/LDS) role to the domain controller by using Server Manager.
Answer: A
Explanation:
Install the Active Directory Schema Snap-In
You can use this procedure to first register the dynamic-link library (DLL) that is required for the Active Directory Schema snap-in. You can then add the snap-in to Microsoft Management Console (MMC). To install the Active Directory Schema snap-in:
1. To open an elevated command prompt, click Start, type command prompt and then right-click Command Prompt when it appears in the Start menu. Next, click Run as administrator and then click OK. To open an elevated command prompt in Windows Server 2012 R2, click Start, type cmd, right click cmd and then click Run as administrator
2. Type the following command, and then press ENTER: regsvr32 schmmgmt.dll
3. Click Start, click Run, type mmc and then click OK
4. On the File menu, click Add/Remove Snap-in
5. Under Available snap-ins, click Active Directory Schema, click Add and then click OK
6. To save this console, on the File menu, click Save
7. In the Save As dialog box, do one of the following:
* To place the snap-in in the Administrative Tools folder, in File name, type a name for the snap-in, and then click Save.
* To save the snap-in to a location other than the Administrative Tools folder, in Save in, navigate to a location for the snap-in. In File name, type a name for the snap-in, and then click Save.
QUESTION 179
Your network contains a domain controller that is configured as a DNS server. The server hosts an Active Directory-integrated zone for the domain. You need to reduce how long it takes until stale records are deleted from the zone. What should you do?
A. From the configuration directory partition of the forest, modify the tombstone lifetime.
B. From the configuration directory partition of the forest, modify the garbage collection interval.
C. From the aging properties of the zone, modify the no-refresh interval and the refresh interval.
D. From the start of authority (SOA) record of the zone, modify the refresh interval and the expire interval.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Scavenging automates the deletion of old records. When scavenging is enabled, then you should also change the no-refresh and refresh intervals of the aging properties of the zone else it may take too long for stale records to be deleted and the size of the DNS database can become large and have an adverse effect on performance.
QUESTION 180
You have an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. You have a domain controller named Server1 that is configured as a DNS server. Server1 hosts a standard primary zone for contoso.com. The DNS configuration of Server1 is shown in the exhibit. You discover that stale resource records are not automatically removed from the contoso.com zone. You need to ensure that the stale resource records are automatically removed from the contoso.com zone. What should you do?

A. Set the scavenging period of Server1 to 0 days.
B. Modify the Server Aging/Scavenging properties.
C. Configure the aging properties for the contoso.com zone.
D. Convert the contoso.com zone to an Active Directory-integrated zone.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Scavenging or aging as it is also known as automates the deletion of old records. When scavenging is disabled, these records must be deleted manually or the size of the DNS database can become large and have an adverse effect on performance. In the exhibit it shows that scavenging is enabled on Server1, thus you should configure the aging properties for the zone.
QUESTION 181
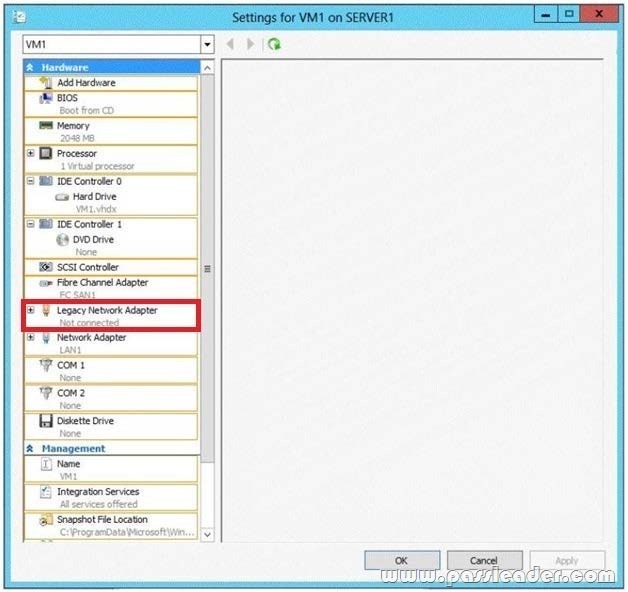
Hotspot Question
Your network contains two servers named Server1 and Server2 that run Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has the Hyper-V server role installed. Server2 has the Windows Deployment Services server role installed. On Server1, you have a virtual machine named VM1. You plan to deploy an image to VM1 by using Windows Deployment Services (WDS). You need to ensure that VM1 can connect to Server1 by using PXE. Which settings should you configure on VM1? To answer, select the appropriate settings in the answer area.

Answer:
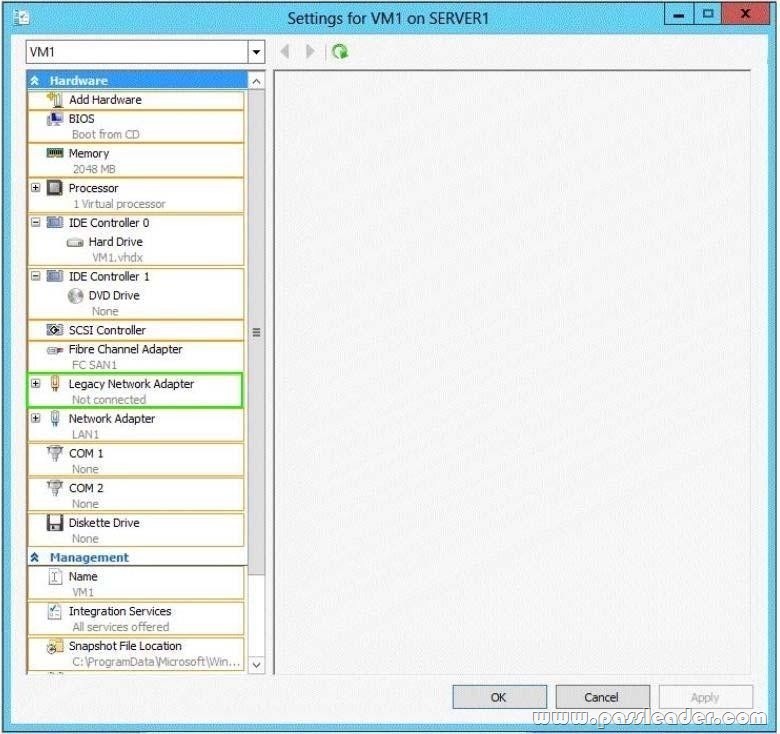
Explanation:
Virtual machines can be deployed to Hyper-V using Windows Deployment Services (WDS). To accomplish this requires the proper WDS infrastructure be in place and that the VM PXE boot using a Legacy Network Adapter. By default, there is only a “Standard Network Adapter” installed on the Virtual Machine, but for PXE functionality you will need to add a “Legacy Network Adapter”. Go to the “Legacy Network Adapter” that you just added and specify that it should use the Virtual Switch that you just created. Last but not least, you should change the BIOS boot priority to make sure that the Virtual Machine always tries to boot first using the “Legacy Network Adapter”. Just select the “Legacy Network Adapter” and move it to the top using the buttons.
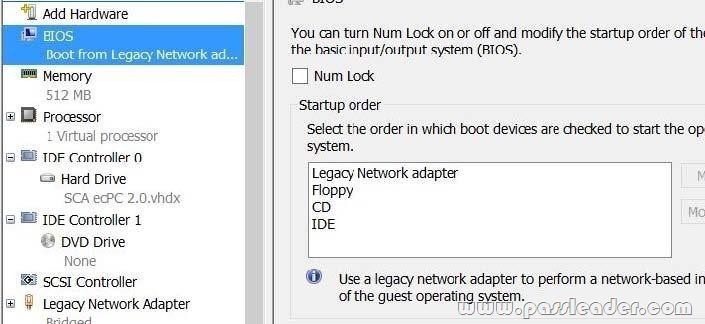
Start your Virtual Machine and now PXE boot should work.
http://www.danielclasson.com/guide-how-to-get-pxe-boot-to-work-in-hyper-v/
http://blogs.technet.com/b/askcore/archive/2008/11/25/installing-a-vm-operating-system-using-a-legacy-network-adapter-and-pxe-boot.aspx
QUESTION 182
Hotspot Question
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. You need to identify whether the Company attribute replicates to the global catalog. Which part of the Active Directory partition should you view? To answer, select the appropriate Active Directory object in the answer area.
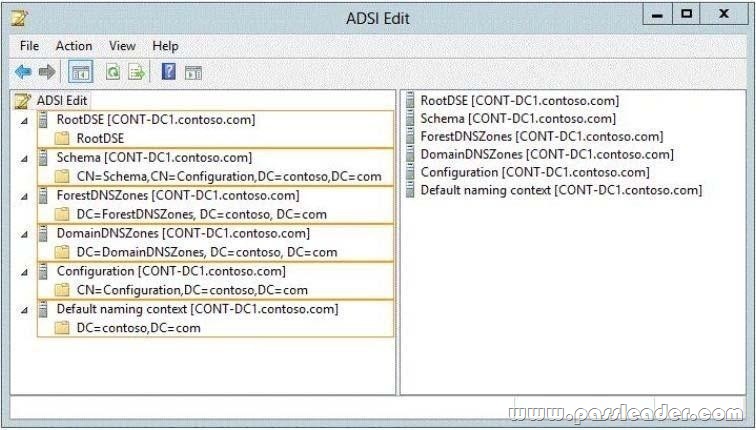
Answer:
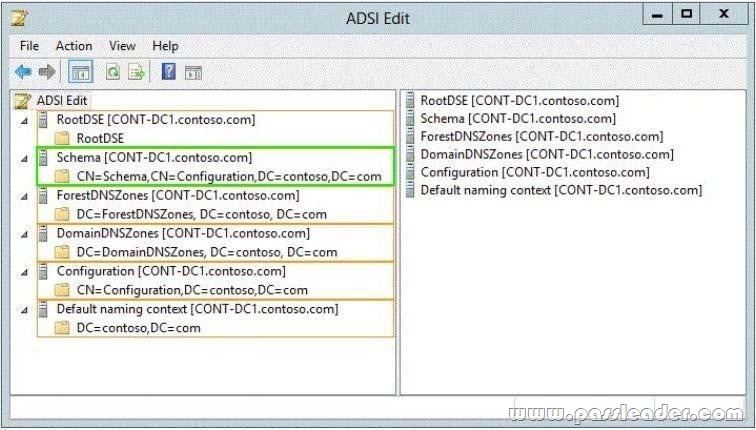
Explanation:
Schema – Contains the Schema container, which stores class and attribute definitions for all existing and possible Active Directory objects in cn=schema,cn=configuration,dc=forestRootDomain. Updates to this container are replicated to all domain controllers in the forest. You can view the contents of the Schema container in the Active Directory Schema console.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc961591.aspx
QUESTION 183
Hotspot Question
You have a server named Server1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2 and has the Windows Deployment Services (WDS) server role installed. You install the DHCP Server server role on Server1. You need to ensure that Server1 can respond to DHCP clients and WDS clients. What should you configure for the DHCP service and the WDS service? To answer, configure the appropriate options in the answer area.

Answer:
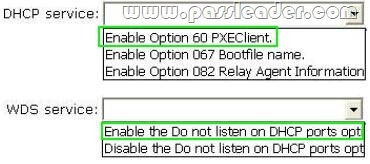
Explanation:
Traditionally, only DHCP listened on port UDP 67, but now WDS also listens on port UDP 67 WDS and DHCP are installed on the same server: You must tell WDS not to listen on port UDP 67, leaving it available for DHCP traffic only. But then how does the client find the WDS server? You set option 60 in DHCP. The DHCP option 60, when set to “PXEClient” is used only to instruct the PXE clients to try to use a PXE Service bound on UDP port 4011. Actually, if there is a bootp or dhcp service bound on UDP port 67 of an host (usually called a server), a PXE service cannot bind on that port on that host. Since the PXE Service uses BOOTP/DHCP packets to send the options 66 and 67 to the clients, it needs to be able to bind to the associated port (bootps) or to an alternated port (4011) that the clients know they must use as the alternate port. And to instruct the clients to use this alternate port, you have to set dhcp option 60 to “PXEClient”. If Windows Deployment Services and DHCP are running on the same computer, configuring Windows Deployment Services to not respond to any client computers will not work. This is because although Windows Deployment Services will not respond, DHCP will. You should disable WDS if you have both installed and using DHCP.
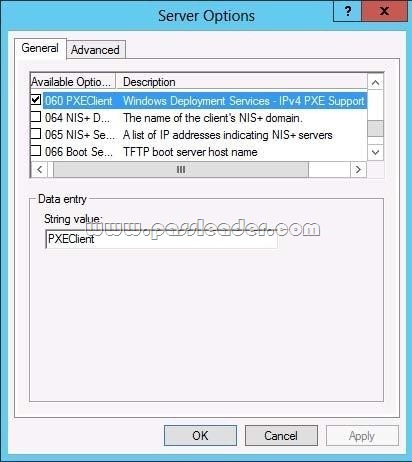
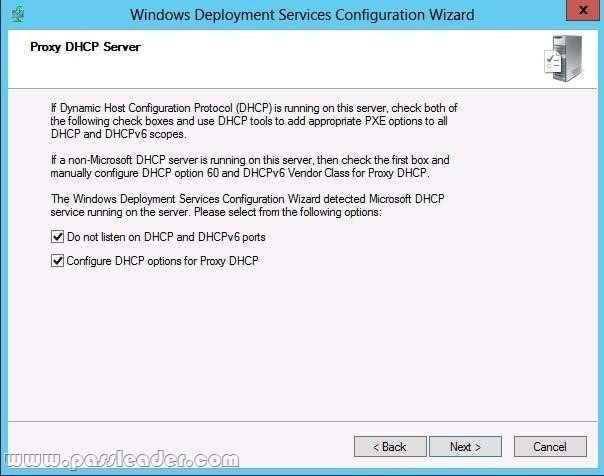
To configure Windows Deployment Services to run on the same computer as Microsoft DHCP: Right-click the server and click Properties. On the DHCP tab, select Do not listen on port 67 and Configure DHCP Option #60 Tag to PXEClient. This procedure does the following: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\WDSServer\Parameters\UseDhcpPorts to 0. Adds the option 60 PXEClient tag to all of your DHCP scopes.
http://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/DHCP-Option-60-Configuratio-2cad825d
QUESTION 184
Hotspot Question
You have a server named Server1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2. A user named Admin1 is a member of the local Administrators group. You need to ensure that Admin1 receives a User Account Control (UAC) prompt when attempting to open Windows PowerShell as an administrator. Which setting should you modify from the Local Group Policy Editor? To answer, select the appropriate setting in the answer area.

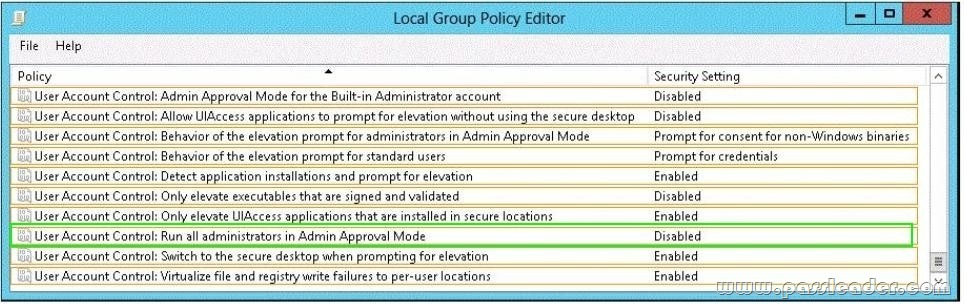
QUESTION 185
You have a server that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. The server contains the disks configured as shown in the following table.

You need to create a volume that can store up to 3 TB of user files. The solution must ensure that the user files are available if one of the disks in the volume fails. What should you create?
A. a storage pool on Disk 2 and Disk 3
B. a spanned volume on Disk 2 and Disk 3
C. a mirrored volume on Disk 1 and Disk 3
D. a mirrored volume on Disk 2 and Disk 3
E. a RAID-5 volume on Disk 1, Disk 2, and Disk 3
F. a storage pool on Disk 1 and Disk 3
G. a spanned volume on Disk 0 and Disk 4
H. a mirrored volume on Disk 1 and Disk 4
Answer: D
QUESTION 186
You have a server that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. The server contains the disks configured as shown in the following table.

You need to create a volume that can store up to 3 TB of user files. The solution must ensure that the user files are available if one of the disks in the volume fails. What should you create?
A. A mirrored volume on Disk 1 and Disk 4
B. A storage pool on Disk 2 and Disk 3
C. A storage pool on Disk 1 and Disk 3
D. A mirrored volume on Disk 2 and Disk 3
Answer: D
Explanation:
A mirrored volume provides an identical twin of the selected volume. All data written to the mirrored volume is written to both volumes, which results in disk capacity of only 50 percent. Any volume can be mirrored, including the system and boot volumes. The disk that you select for the shadow volume does not need to be identical to the original disk in size, or in its number of tracks and cylinders. This means that you do not have to replace a failed disk with an identical model. The unused area that you select for the shadow volume cannot be smaller than the original volume. If the area that you select for the shadow volume is larger than the original, the extra space on the shadow disk can be configured as another volume. Dynamic disks provide features that basic disks do not, such as the ability to create volumes that span multiple disks (spanned and striped volumes) and the ability to create fault-tolerant volumes (mirrored and RAID-5 volumes). The following operations can be performed only on dynamic disks:
– Create and delete simple, spanned, striped, mirrored, and RAID-5 volumes.
– Extend a simple or spanned volume.
– Remove a mirror from a mirrored volume or break the mirrored volume into two volumes.
– Repair mirrored or RAID-5 volumes.
– Reactivate a missing or offline disk.
You need at least two dynamic disks to create a mirrored volume. Mirrored volumes are fault tolerant and use RAID-1, which provides redundancy by creating two identical copies of a volume. Mirrored volumes cannot be extended. Both copies (mirrors) of the mirrored volume share the same drive letter.

http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc779765%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa363785%28v=vs.85%29.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc938487.aspx
QUESTION 187
Hotspot Question
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named adatum.com. All domain controllers run Windows Server 2012 R2. All client computers run Windows 7. The computer accounts for all of the client computers are located in an organizational unit (OU) named OU1. An administrator links a Group Policy Object (GPO) to OU1. The GPO contains several application control policies. You discover that the application control policies are not enforced on the client computers. You need to modify the GPO to ensure that the application control policies are enforced on the client computers. What should you configure in the GPO? To answer, select the appropriate service in the answer area.
Answer:

Explanation:
Does AppLocker use any services for its rule enforcement? Yes, AppLocker uses the Application Identity service (AppIDSvc) for rule enforcement. For AppLocker rules to be enforced, this service must be set to start automatically in the GPO.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee619725%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 188
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains three servers named Server1, Served, and Server3. You create a server group named ServerGroup1. You discover the error message shown in the following exhibit. (Click the Exhibit button.)

You need to ensure that Server2 can be managed remotely by using Server Manager. What should you do?
A. On DC1, run the Enable-PSSessionConfiguration cmdlet.
B. On Server2, run the Add-Computer cmdlet.
C. On Server2/ modify the membership of the Remote Management Users group.
D. From Active Directory Users and Computers, add a computer account named Server2, and then restart Server2.
Answer: C
Explanation:
This is a security issue. To be able to access Server2 remotely through Server Manager the user need to be a member of the Remote Management Users group.
Incorrect:
Not A: the Enable-PSSessionConfiguration.This is an advanced cmdlet that is designed to be used by system administrators to manage customized session configurations for their users.
Reference: Enable-ServerManagerStandardUserRemoting
QUESTION 189
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has the Hyper-V server role installed. An iSCSI SAN is available on the network. Server1 hosts four virtual machines named VM1, VM2, VM3, and VM4. You create a LUN on the SAN. You need to provide VM1 with access to the LUN. The solution must prevent other virtual machines from accessing the LUN. What should you configure?
A. A fixed-size VHDX
B. A fixed-size VHD
C. A dynamically expanding VHD
D. A dynamically expanding VHDX
E. A pass-through disk
Answer: E
Explanation:
You can use physical disks that are directly attached to a virtual machine as a storage option on the management operating system. This allows virtual machines to access storage that is mapped directly to the server running Hyper-V without first configuring the volume. The storage can be either a physical disk which isinternal to the server, or a SAN logical unit number (LUN) that is mapped to the server (a LUN is a logical reference to a portion of a storage subsystem). The virtual machine must have exclusive access to the storage, so the storage must be set in an Offline state in Disk Management. The storage is not limited insize, so it can be a multitera byte LUN. When using physical disks that are directly attached to a virtual machine, you should be aware of the following:
– This type of disk cannot be dynamically expanded.
– You cannot use differencing disks with them.
– You cannot take virtual hard disk snapshots.
Note:
If you are installing an operating system on the physical disk and it is in an Online state before the virtual machine is started, the virtual machine will fail to start. You must store the virtual machine configuration file inan alternate location because the physical disk is used by the operating system installation. For example,locate the configuration file on another internal drive on the server running Hyper-V.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee344823%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
http://blogs.technet.com/b/askcore/archive/2008/10/24/configuring-pass-through-disks-inhyper-v.aspx
QUESTION 190
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a print server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 contains a local group named Group1. You share a printer named Printer1 on Server1. You need to configure Printer1 to meet the following requirements:
– Ensure that the members of Group1, the Server Operators group, the Administrators group, and the Print Operators group can send print jobs to Printer1.
– Prevent other users from sending print jobs to Printer1.
Which two actions should you perform? (Each correct answer presents part of the solution. Choose two.)
A. Assign the Print permission to the Server Operators group.
B. Remove the permissions for the Creator Owner group.
C. Remove the permissions for the Everyone group.
D. Assign the Print permission to Group1.
E. Assign the Print permission to the Administrators group.
Answer: CD
Explanation:
C: To prevent other users from sending print jobs to Printer1.
D: To enable Group1 to send print jobs.
Note: The Server Operators group, the Administrators group, and the Print Operators group are all built-in and already have permissions to send print jobs.
QUESTION 191
You have a new server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has two dual-core processors and 32 GB of RAM. You install the Hyper-V server role on Server1. You create two virtual machines on Server1 that each have 8 GB of memory. You need to minimize the amount of time it takes for both virtual machines to access memory. What should you configure on each virtual machine?
A. Resource control
B. Dynamic Memory
C. NUMA topology
D. Memory weight
Answer: C
Explanation:
Windows Server 2012 introduced support for projecting a virtual NUMA topology into Hyper-V virtual machines. This capability can help improve the performance of workloads running on virtual machines that are configured with large amounts of memory.
QUESTION 192
Hotspot Question
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. Domain controllers run either Windows Server 2008 R2 or Windows Server 2012 R2. All client computers run Windows 8. All computer accounts are located in an organizational unit (OU) named OU1. You create a Group Policy Object (GPO) that contains several AppLocker rules. You link the GPO to OU1. You need to ensure that the AppLocker rules apply to all of the client computers. What should you configure in the GPO? To answer, select the appropriate service in the answer area.

QUESTION 193
Hotspot Question
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. Technicians use Windows Deployment Services (WDS) to deploy Windows Server 2012 R2. The network contains a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has the Hyper-V server role installed. You need to ensure that you can use WDS to deploy Windows Server 2012 R2 to a virtual machine named VM1. Which settings should you configure? To answer, select the appropriate settings in the answer area.

QUESTION 194
Hotspot Question
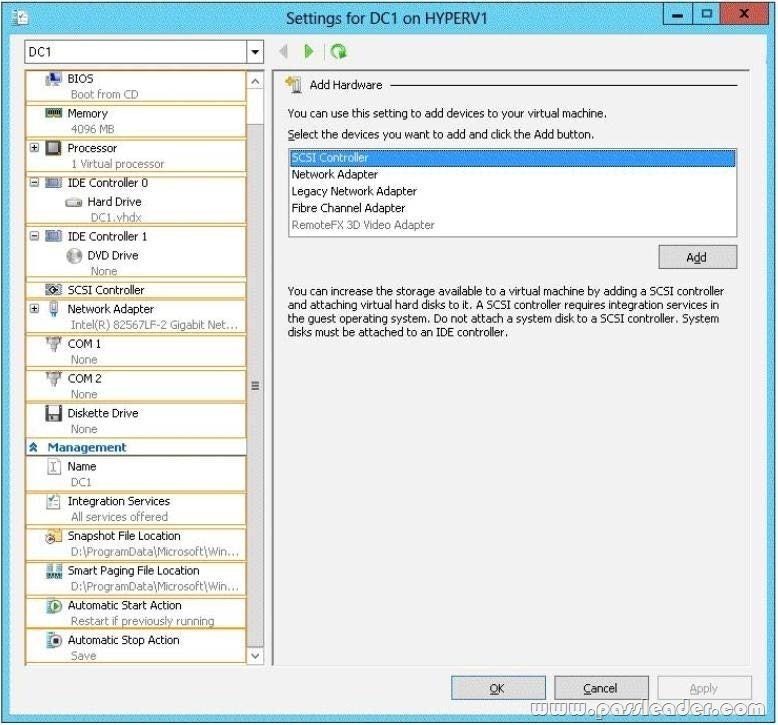
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a member server named Hyperv1 and a domain controller named DC1. Hyperv1 has the Hyper-V server role installed. DC1 is a virtual machine on Hyperv1. Users report that the time on their client computer is incorrect. You log on to DC1 and verify that the time services are configured correctly. You need to prevent time conflicts between the time provided by DC1 and other potential time sources. What should you configure? To answer, select the appropriate object in the answer area.
QUESTION 195
You perform a Server Core Installation of Windows Server 2012 R2 on a server named Server1. You need to add a graphical user interface (GUI) to Server1. Which tool should you use?
A. the dism.exe command
B. the Add-WindowsFeature cmdlet
C. the imagex.exe command
D. the setup.exe command
E. the ocsetup.exe command
F. the Add-WindowsPackage cmdlet
G. the Install-Module cmdlet
H. the Install-RoleService cmdlet
Answer: AB
Explanation:
Add-WindowsFeature -The Add-WindowsFeature cmdlet allows you to install specified roles, role services, and features on a computer that is running Windows Server 2008 R2.
Install-WindowsFeature -Installs one or more Windows Server roles, role services, or features on either the local or a specified remote server that is running Windows Server 2012 R2. This cmdlet is equivalent to and replaces Add-WindowsFeature, the cmdlet that was used to install roles, role services, and features in Windows Server 2008 R2.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh824822.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd744582(v=ws.10).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/jj205467(v=wps.620).aspx
QUESTION 196
You have a server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 has the Hyper-V server role installed. You need to configure storage for a virtual machine to meet the following requirements:
– Support up to 3 TB of data on a single hard disk.
– Allocate disk space as needed.
– Use a portable storage format.
What should you configure?
A. A pass-through disk
B. A fixed-size VHD
C. A dynamically expanding VHD
D. A fixed-size VHDX
E. A dynamically expanding VHDX
Answer: E
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh831446.aspx
Support for virtual hard disk storage capacity of up to 64TB. VHD max is 2TB.
QUESTION 197
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. All user accounts are in an organizational unit (OU) named Employees. You create a Group Policy Object (GPO) named GP1. You link GP1 to the Employees OU. You need to ensure that GP1 does not apply to the members of a group named Managers. What should you configure?
A. The Security settings of Employees
B. The WMI filter for GP1
C. The Block Inheritance option for Employees
D. The Security settings of GP1
Answer: D
Explanation:
A. Wrong Group.
B. Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) filters allow you to dynamically determine the scope of Group Policy Objects (GPOs) based on attributes of the target computer.
C. Blocking inheritance prevents Group Policy Objects (GPOs) that are linked to higher sites, domains, or organizational units from being automatically inherited by the child-level.
D. Set Managers to – Members of this security group are exempt from this Group Policy Object.
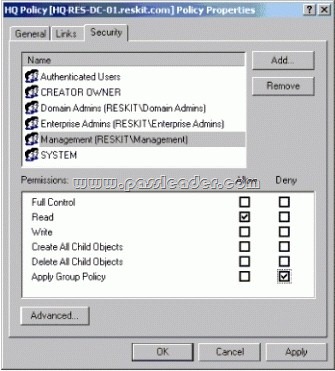
Note: Security settings. You use the Security Settings extension to set security options for computers and users within the scope of a Group Policy Object. You can define local computer, domain, and network security settings. Figure belows shows an example of the security settings that allow everyone to be affected by this GPO except the members of the Management group, who were explicitly denied permission to the GPO by setting the Apply Group Policy ACE to Deny. Note that if a member of the Management group were also a member of a group that had an explicit Allow setting for the Apply Group Policy ACE, the Deny would take precedence and the GPO would not affect the user.

http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb742376.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc786636(WS.10).aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731076.aspx
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc779036(v=ws.10).aspx
QUESTION 198
You have a virtual machine named VM1. You install Windows Server 2012 R2 on VM1. You plan to use VM1 as an image that will be distributed to sales users to demonstrate the features of a custom application. The custom application only requires the Web Server (IIS) server role to be installed. You need to ensure that the VHD file for VM1 only contains the required Windows Server 2012 R2 source files. Which tool should you use?
A. dism.exe
B. ocsetup.exe
C. imagex.exe
D. servermanagercmd.exe
Answer: A
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/dd490958.aspx
You can use DISM to:
– Add, remove, and enumerate packages and drivers.
– Enable or disable Windows features.
– Apply changes based on the offline servicing section of an unattend.xml answer file.
– Configure international settings.
– Upgrade a Windows image to a different edition.
– Prepare a Windows PE image.
– Take advantage of better logging.
– Service down-level operating systems like Windows Vista with SP1 and Windows Server 2008.
– Service all platforms (32-bit, 64-bit, and Itanium).
– Service a 32-bit image from a 64-bit host and service a 64-bit image from a 32-bit host.
– Make use of old Package Manager scripts.
QUESTION 199
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a server named Server1. Server1 runs Windows Server 2012 R2 and has the Hyper-V server role installed. On Server1, you create and start a virtual machine named VM1. VM1 is configured as shown in the following table.
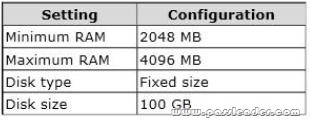
You plan to create a snapshot of VM1. You need to recommend a solution to minimize the amount of disk space used for the snapshot of VM1. What should you do before you create the snapshot?
A. Run the Stop-VM cmdlet.
B. Run the Convert-VHD cmdlet.
C. Decrease the Maximum RAM
D. Decrease the Minimum RAM.
Answer: A
Explanation:
What are virtual machine snapshots?
Virtual machine snapshots capture the state, data, and hardware configuration of a running virtual machine.
What are snapshots used for?
Snapshots provide a fast and easy way to revert the virtual machine to a previous state. For this reason, virtual machine snapshots are intended mainly for use in development and test environments. Having an easy way to revert a virtual machine can be very useful if you need to recreate a specific state or condition so that you can troubleshoot a problem. There are certain circumstances in which it may make sense to use snapshots in a production environment. For example, you can use snapshots to provide a way to revert a potentially risky operation in a production environment, such as applying an update to the software running in the virtual machine.
How are snapshots stored?
Snapshot data files are stored as .avhd files. Taking multiple snapshots can quickly consume storage space. In the first release version of Hyper-V (KB950050) and in Hyper-V in Windows Server 2008 Service Pack 2, snapshot, snapshot data files usually are located in the same folder as the virtual machine by default. In Hyper-V in Windows Server 2008 R2, the files usually are located in the same folder as the virtual hard disk. The following exceptions affect the location of the snapshot data files: If the virtual machine was imported with snapshots, they are stored in their own folder. If the virtual machine has no snapshots and you configure the virtual machine snapshot setting, all snapshots you take afterwards will be stored in the folder you specify.
http://technet.microsoft.com/pt-pt/library/dd560637%28v=ws.10%29.aspx
QUESTION 200
Your network contains an Active Directory domain named contoso.com. The domain contains a file server named Server1 that runs Windows Server 2012 R2. Server1 contains a shared folder named Share1. Share1 contains the home folder of each user. All users have the necessary permissions to access only their home folder. The users report that when they access Share1, they can see the home folders of all the users. You need to ensure that the users see only their home folder when they access Share1. What should you do from Server1?
A. From Windows Explorer, modify the properties of the volume that contains Share1.
B. From Server Manager, modify the properties of the volume that contains Share1.
C. From Server Manager, modify the properties of Share1.
D. From Windows Explorer, modify the properties of Share1.
Answer: C
Explanation:
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc784710(v=ws.10).aspx
Access based enumeration needs to be enabled:

Get the newest PassLeader 70-410 VCE dumps here: http://www.passleader.com/70-410.html (512 Q&As Dumps –> 528 Q&As Dumps)
And, DOWNLOAD the newest PassLeader 70-410 PDF dumps from Cloud Storage for free: https://drive.google.com/open?id=0B-ob6L_QjGLpfnJzOE1fWnlJOWVtaE93SnJNT3gtaTNYYnVpZkw5THBSMWRKbFlfaXh1azg